DORA: What Financial IT Must Know
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) entered into application across the European Union on 17 January 2025, reshaping how financial institutions manage cyber and operational risk [1]. Although the United...
Having an issue with EIGRP? Network automation can help you troubleshoot EIGRP routing problems more effectively.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Protocol (EIGRP) is a Cisco proprietary distance vector routing protocol commonly used in modern networks. It speeds up convergence by storing backup routes in the topology table and using them when a primary route fails. There are many common failures that may occur to inhibit successful EIGRP routing, for example:
Network automation can help you troubleshoot EIGRP routing problems more effectively. You can instantly create a Dynamic Network Map to target an EIGRP AS, then you can drill down with automation to diagnose neighbor adjacencies, route table changes, and configuration discrepancies in real-time. This same methodology can be applied towards troubleshooting any other dynamic routing protocols including OSPF, IS-IS, RIPv2, and BGP.
Map the EIGRP AS Instantly
Before you can drill-down and understand the problem, you’ll want to identify the EIGRP-enabled routers in the network which should be forming neighbor relationships and exchanging routes. With NetBrain, one method of targeting the problem is to map around the EIGRP Autonomous System (AS) which is having the issue. You can do this with a few clicks. After mapping the relevant EIGRP AS, you can dynamically add neighbors to the map to expand the scope of your visibility.

Instantly Map an EIGRP Autonomous System
As you expand the map, you can turn on ‘highlighting’ to see the boundaries of each EIGRP AS. Both the interior and exterior gateway protocols will be highlighted automatically.

Automatically Color-Code the Map with Routing Design
Troubleshoot EIGRP with Automated Diagnosis
NetBrain provides a way for you to collect and analyze data from the network without having to log into a bunch of switches serially and type in a string of show commands. NetBrain has several built-in apps designed to automate routing diagnoses. Most importantly, you can easily write your own apps to automate your most common troubleshooting tasks. These apps leverage the map as the ‘canvas’ for your targeted data analysis.
Recommended App: Map EIGRP Neighbor Status
This app adds the functionality to annotate the current EIGRP neighbor status on the map using the show ip eigrp neighbors IOS command. This can help you immediately identify if any adjacent routers are failing to form neighbor relationships.

Map EIGRP Neighbor Relationships
Highlight EIGRP Configuration
When you troubleshoot EIGRP or other dynamic routing protocols, you need to understand the relevant configuration on each device. To save you time in digesting lengthy config files on each device, this app is designed to parse the EIGRP configuration, route summary, and route manipulation from the configuration files for you automatically. The output is appended to each device on the map as a note, for quick reference.

Annotate EIGRP Configuration on the Map
Monitor Running Status to Troubleshoot EIGRP
The real-time status of EIGRP – including neighbors, EIGRP routes, EIGRP prefix, and the EIGRP CPU/memory – can provide important insights. This information can help you understand whether routes are missing from the route tables, or if routes are being redistributed properly. This app, when running, will continuously monitor real-time EIGRP status and display the current status under each router on the map.

Display Real-Time EIGRP Status on the Map
The historical data for every metric is automatically captured, plotted, and saved directly to the Qmap file for as long as the app is running. Monitoring for fluctuations in this data can provide clues about what’s going on.

Highlight EIGRP Parameters
In order to calculate a metric for evaluating path selection, EIGRP adds together weighted values of different network link characteristics, which include:
Various constants (K1 through K5) are able to be set by a user to produce varying routing behaviors. However by default, only delay and bandwidth are used in the weighted formula to produce a single 32bit metric:
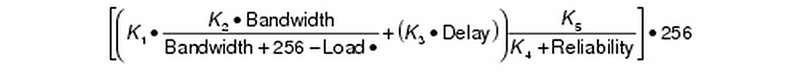
When K5 is equal to 0 then [K5/( K4 + reliability)] is defined to be 1
These K-Values as well as the Hello/Hold-down Timers are configurable EIGRP parameters which may influence EIGRP performance. The Highlight EIGRP Parameters app is designed to quickly identify the existing parameters on each device, and draw a note on the map to reflect them.

Automatically Annotate the Map to Reflect K-Values and Hello/Hold Timer Values
Compare Historical Routing Data
An unverified routing or configuration change may have disastrous effects on the network. That’s why sometimes the best question to ask while you troubleshoot EIGRP is ‘what changed?’ This app can find specific changes in configuration, route tables, EIGRP neighbor tables, and much more. It leverages historical benchmark data (collected automatically by the system) for the comparison.
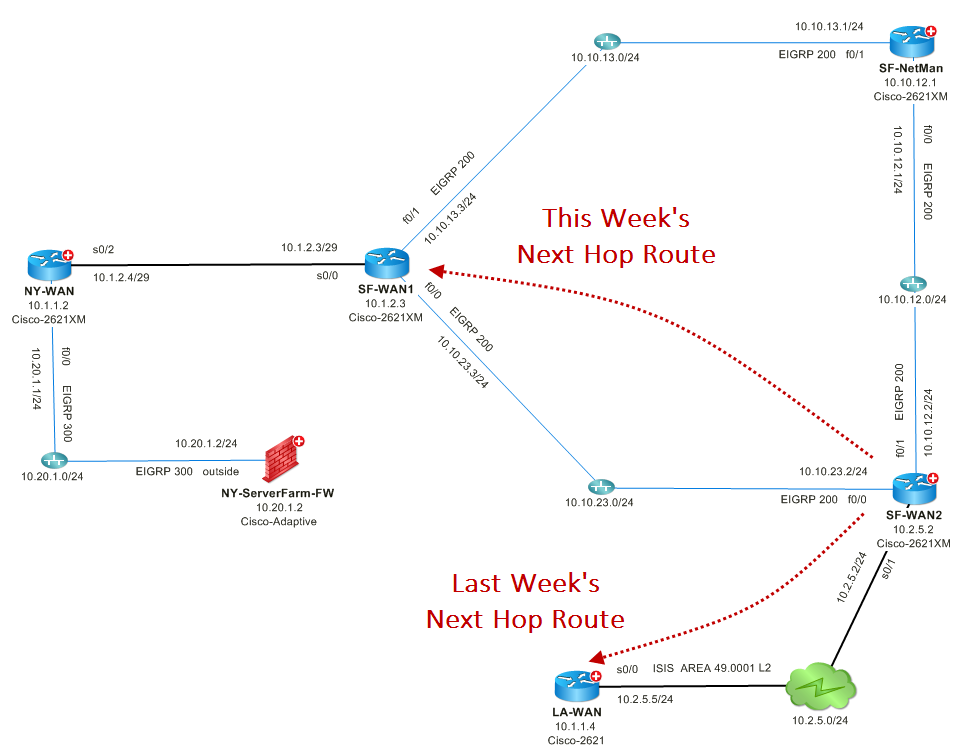
Compare Route Tables Visually
These are just a few ways automation can help when you suspect a routing issue. If you want to try these features out for yourself, you can checkout our technology labs – accessible inside NetBrain’s Instant Trial!