Using Runbook to Document Map-Based Activities
NetBrain Runbook provides a visual way to codify network troubleshooting process into an executable, reusable, and documentable workflow, to elevate collaboration efficiency. Besides, tribal leaders can digitize their knowledge into a runbook template to streamline best practices for the entire team.
Use Case
▪Record Activities and Process
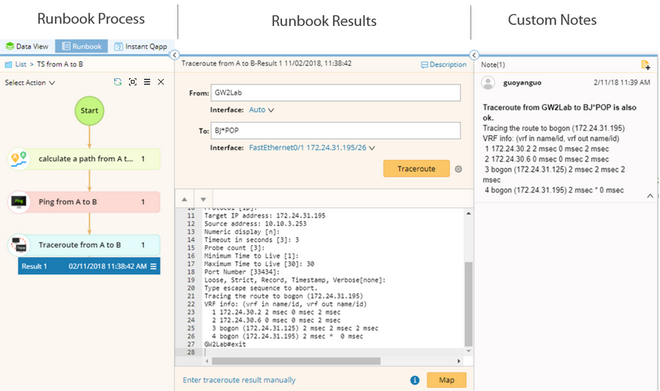
For example, end users run Qapps, execute CLI commands, or use Ping/Traceroute to troubleshoot a problematic area. These actions are instantly recorded in a Default Runbook, and each action can be annotated with thoughts or analysis to document the diagnosis process.
Example: Execute a Runbook to Troubleshoot A/B Path Issue
▪Share Knowledge and Know-How
For example, to proactively take measures for network problems that might re-occur, power users create a Runbook Template and continue to improve it, to share best practices and know-how with junior engineers.
▪Re-executable to Maximize Data Value.
For example, Tier 1 engineers execute CLI commands to troubleshoot problematic devices on a map, document the diagnosis and escalate the issue by mentioning next-level users in the runbook. Tier 2 engineers re-execute the runbook, and continue to add a Compare node to evaluate data changes between the two CLI outputs, and then escalate to Tier 3. Each Tier can continue to build on top of what has been done previously by checking analysis results and notes.
Map-Based Activities
Runbook consists of one or multiple assembled actions. Each action node can be executed individually and repetitively to automate data analysis. On a map, you can start quick automation with any action node first, and further save it as a runbook.

The following action nodes can be either executed independently or assembled in a runbook.
Action |
Description |
|---|---|
Run a single Qapp to perform an automation task. |
|
Run a built-in Qapp to monitor your network health. |
|
Run a group of contextualized Qapps for multistage troubleshooting. |
|
Retrieve live data by executing CLI commands. |
|
Retrieve device data by executing CLI commands or selecting built-in data types, and save the data. |
|
Test the connectivity from one endpoint to another. |
|
Discover and map a routing path between two endpoints. |
|
Path |
Refer to Mapping an A/B path. |
Compare data changes between two different time points, or between two versions of device data. |
|
Free Text |
Annotate a text based on needs, such as describing the usage of each branch. |
