Map A/B Paths for Unicast and Multicast Traffic
The Path Calculator enable users to calculate and visualize traffic paths, both unicast and multicast, to support effective monitoring and troubleshooting of network traffic flows.
Calculate a Unicast Path
- On the search bar, click the path icon
 .
. - Enter the source and the destination IP addresses (device hostnames or DNS names).
 Tip: The 1st Hop Map function can help you choose the first hop.
Tip: The 1st Hop Map function can help you choose the first hop.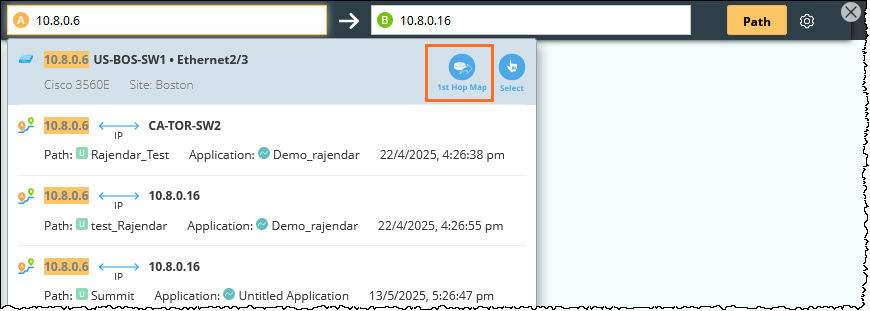
- Click the
 icon and then select
icon and then select  or the
or the  icon to select the path direction. By default, the system calculates one-way paths.
icon to select the path direction. By default, the system calculates one-way paths.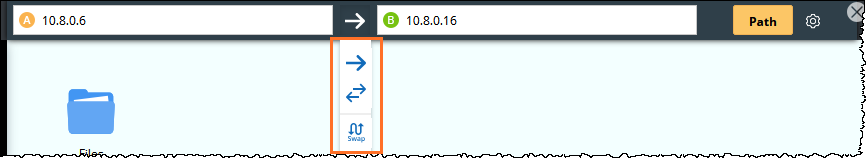

Tip: To quickly swap the source and the destination IP addresses, click the  icon.
icon.
- If an endpoint has multiple gateways, select the correct one from the Gateway list, or select any device's interface with IP as the gateway for the end system.
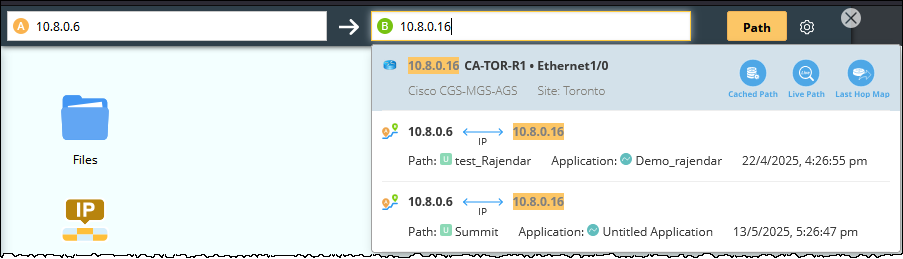

Tip: To configure the data source, protocol, and other advanced settings for path calculation, click the
 icon to make changes. See Path Settings for more reference.
icon to make changes. See Path Settings for more reference.
Note: Only the current device's interface with configured IP can be chosen as the gateway for a network device. 
Tip: You can predefine gateways for end systems in batch in your NetBrain domain. With the definition, the system automatically looks up the matched gateways for the source and destination during a path calculation without having to re-selecting the gateways. See Predefining Gateway Fix-up Rules for details. - Click the Path to start calculating the path. A map is automatically created to draw the Path Hop by Hop.
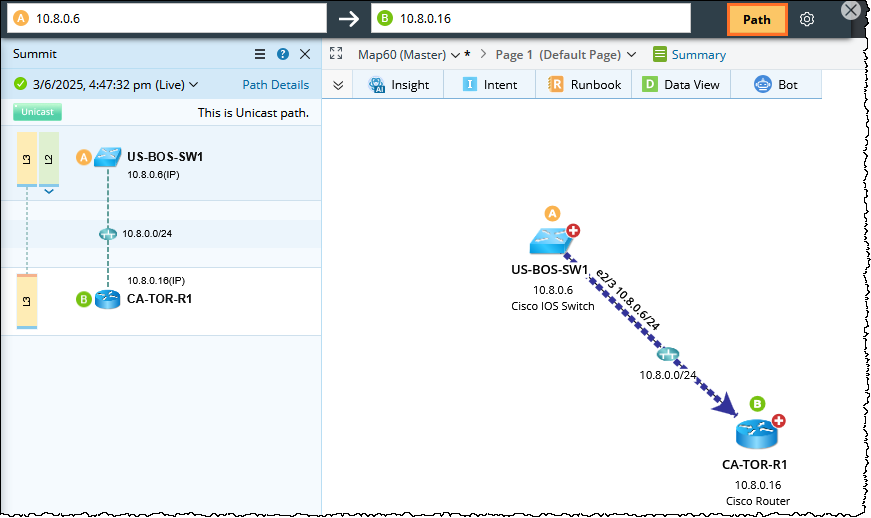

Tip: The system determines which path type to calculate based on the network topology type the traffic goes through. For example, a traffic path goes through an interface with L2, L3, and overlay topology types, and the system will calculate three types of paths (L2 path, L3 path, and overlay path). You can click a path type in the Path Result pane to show the corresponding path on the map.
Note: The technology tag for each Path hop is checked by the path discovery logic.
Example image:

- (Optional) Click the
 icon in the Path Result Pane and select Save Path to save the path to the Path Browser.
icon in the Path Result Pane and select Save Path to save the path to the Path Browser.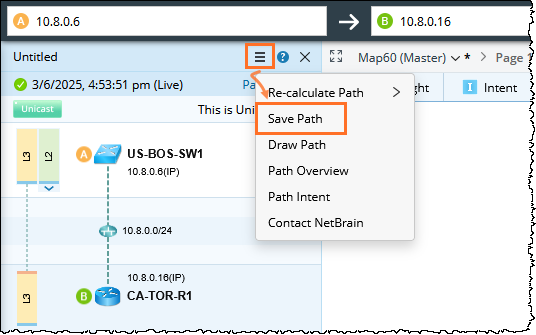
Calculate a Multicast Path
- On the search bar, click the path icon
 .
. - Click the path Setting icon
 and select Multicast as Path type.
and select Multicast as Path type. - Enter the following in the search bar
- Multicast Receiver IP address in the Receiver field.
- Multicast Source IP address in the Source field.
- Group Value in the Group field.

- If a device has multiple gateways, select the correct one from the Gateway list, or select any device's interface with IP as the gateway for the end system.

Tip: To configure the data source, protocol, and other advanced settings for path calculation, click the
 icon to make changes. See Path Settings for more reference.
icon to make changes. See Path Settings for more reference.
Note: Only the current device's interface with configured IP can be chosen as the gateway for a network device. 
Tip: You can predefine gateways for end systems in batch in your NetBrain domain. With the definition, the system automatically looks up the matched gateways for the source and destination during a path calculation without having to re-selecting the gateways. See Predefining Gateway Fix-up Rules for details.
- Click the path to start calculating the path. A map is automatically created to diagram the multicast path.
- (Optional) Click the
 icon in the Path Result Pane and select Save Path to save the path to the Path Browser.
icon in the Path Result Pane and select Save Path to save the path to the Path Browser.
Further operations:
- Viewing Path Results and Details
- View Path Log
- Document Path
- Select the path on the map and click Monitor to monitor the overall health of the devices along the path.
- Run Qapp on the Path
See also: