Kubernetes Visual Manager
This topic describes detailed instructions for enabling visibility into Native Kubernetes clusters, nodes, pods, services, and ingresses, as well as utilizing topology views, data tables, and end-to-end (E2E) path calculations.
Prerequisites
- Administrative access to the Native Kubernetes cluster.
- Access to the NetBrain management interface.
- The Native Kubernetes API server must be reachable from the NetBrain system.
Discover Native Kubernetes Component
NetBrain supports the discovery of your On-premise, including the Kubernetes Cluster, Node, Pod, Ingress, and Service.
To enable this, configure the appropriate Kubernetes Service Account Cluster Role and set up the API server by following the NetBrain Kubernetes Quick Setup Guide. Once configured, initiate network discovery to detect all Kubernetes Components including the Kubernetes Cluster, Node, Pod, Ingress, and Service, as illustrated below.

Feature Scope
The following are the feature scope in the Native Kubernetes Cluster:
- Network Tree
- Context Map
-
Device Details
- Device Properties
- Interface Properties
- Neighbor Topology
- Data Tables
- Calculate End-to-End Paths
- Automate Observability
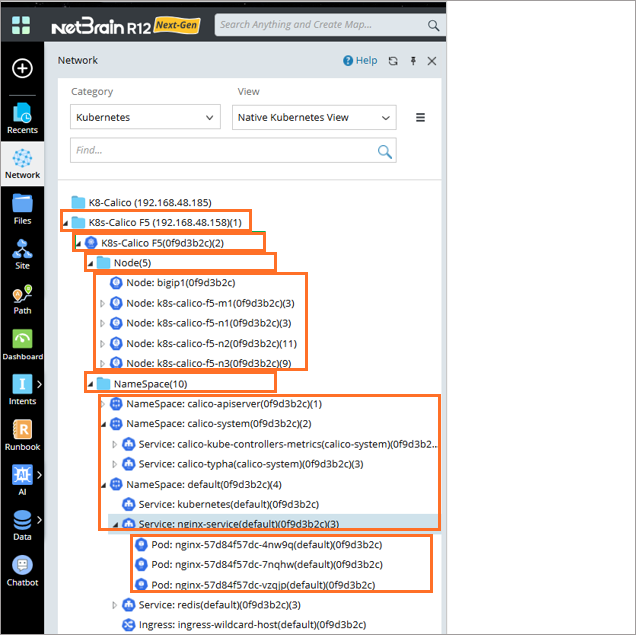
Network Tree Hierarchy
Network Tree provides a structured view, making it easy to locate specific Kubernetes object and understand the resource hierarchy within your Cluster.
The Kubernetes Hierarchy follow these levels:
-
Level 1: <API Server Name>
-
Level 2: <Kubernetes Clusters Name/ID>
-
Level 3: Nodes <Folder>
- Level 4: Kubernetes Pods
-
Level 3: Namespaces <Folder>
-
Level 4: Kubernetes Services
- Level 5: Kubernetes Pods
-
Level 4: Kubernetes Ingresses
-
Level 4: Kubernetes Services
-
Level 3: Nodes <Folder>
-
Level 2: <Kubernetes Clusters Name/ID>
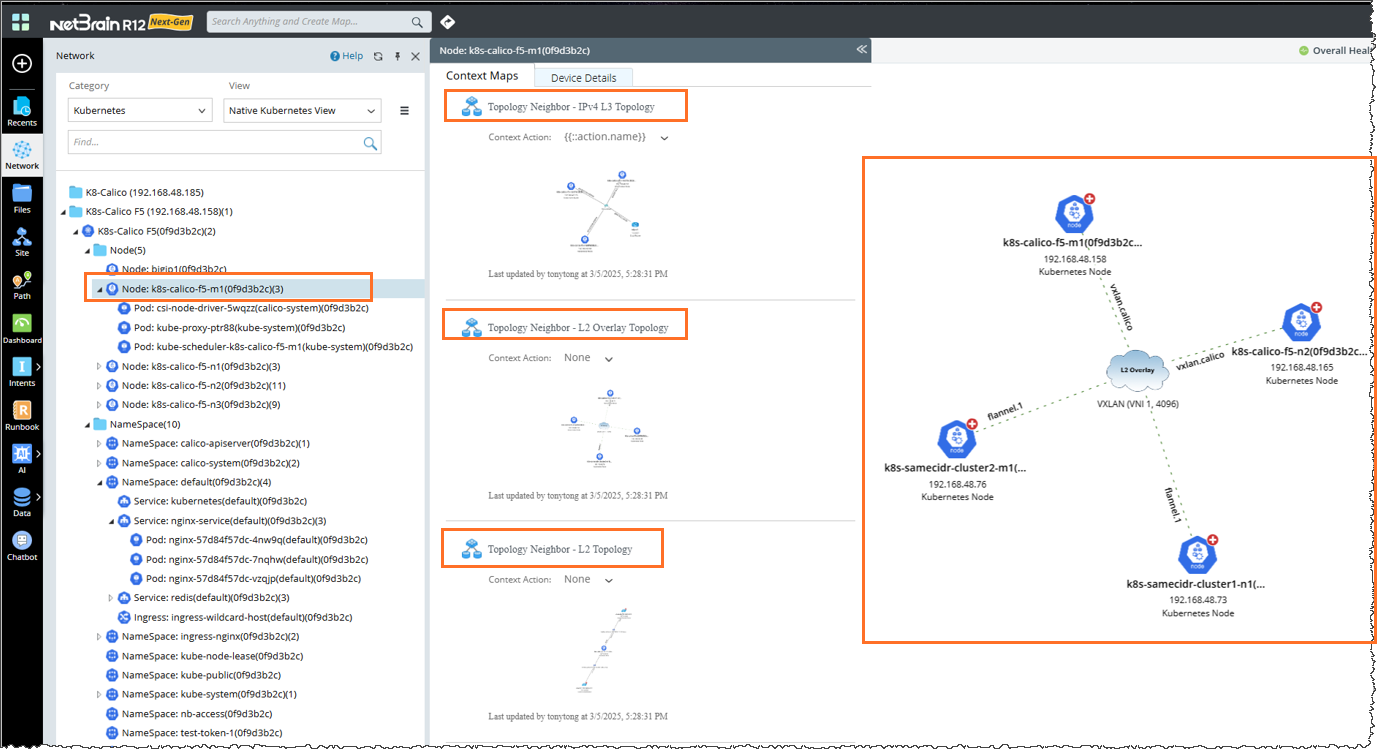
Visualize Connectivity with Context Map
Right-click the node on the map and select View the Context Map. This will display the Context Map, which provides information about Kubernetes Internal/External connectivity. It shows the Dynamic Map based on various scenarios like L3 Topology, L2 Overlay Topology, and L2 Topology.
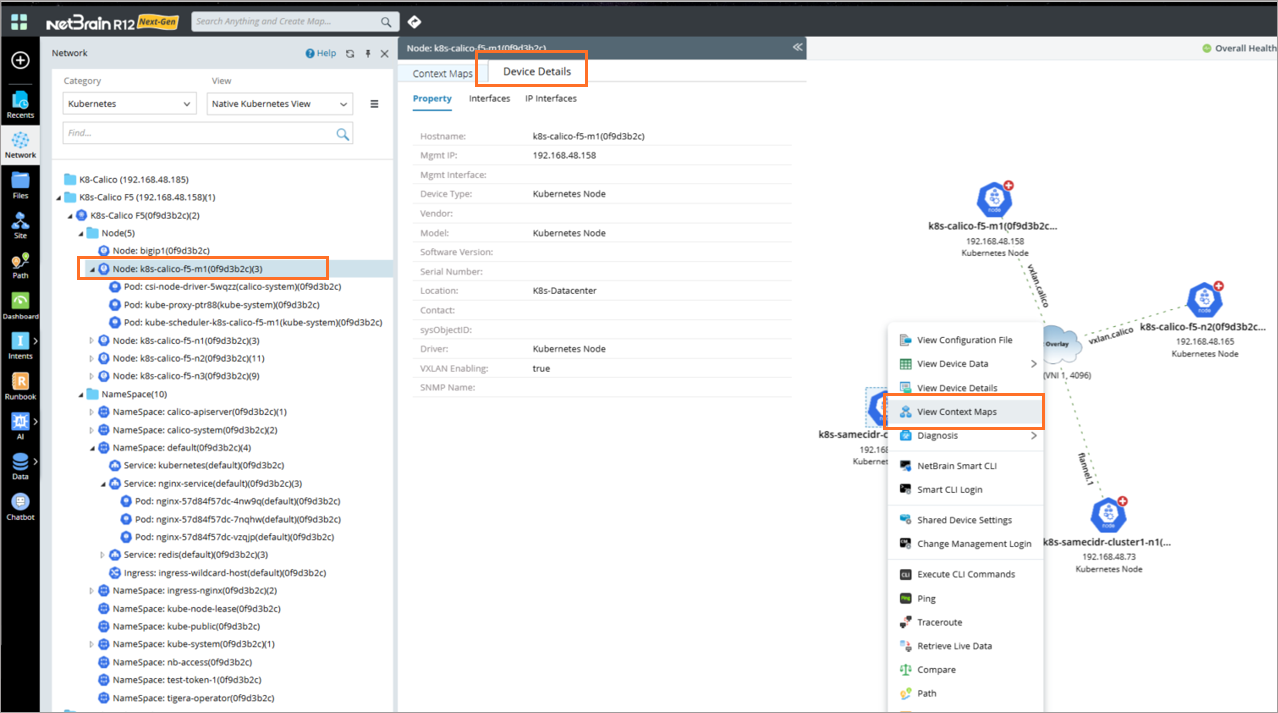
Device Details
Device Details provides basic information about Kubernetes objects, Device properties and Interface Properties.
Device Properties
NetBrain supports the following Kubernetes device types:
- Kubernetes Node
- Kubernetes Pod
- Kubernetes Service
- Kubernetes Ingress
Kubernetes Node
|
Device Property Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Hostname
|
Name of Kubernetes Node. Name is combination of actual name of node and kube-system name sapce id.
|
|
Mgmt IP
|
Management IP of Node
|
Kubernetes Pod
|
Device Property Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Name
|
Name of Kubernetes Pod. Name is combination of actual name of pod and kube-system name sapce id.
|
|
UID
|
Uid of Pod
|
|
Namespace
|
Name space name where the pod belongs
|
|
Resource Version
|
In Kubernetes, resourceVersion is a unique identifier assigned to an API resource instance that changes every time the resource is modified. It helps track updates and ensures consistency when working with Kubernetes objects
|
|
Creation Timestamp
|
The creationTimestamp field in a Kubernetes resource represents the exact time when the object was created
|
|
Labels
|
Labels are key-value pairs assigned to Kubernetes Pod to categorize, organize, and select resources efficiently.
|
Kubernetes Service
| Device Property Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of Kubernetes Service. Name is combination of actual name of Service and kube-system name sapce id. |
| UID | Uid of Service. |
| Namespace | Name space name where the Service belongs. |
| Resource Version | In Kubernetes, resourceVersion is a unique identifier assigned to an API resource instance that changes every time the resource is modified. It helps track updates and ensures consistency when working with Kubernetes objects. |
| Creation Timestamp | The creationTimestamp field in a Kubernetes resource represents the exact time when the object was created |
| API Version | Labels are key-value pairs assigned to Kubernetes Pod to categorize, organize, and select resources efficiently. |
Kubernetes Ingress
|
Device Property Name
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Name
|
Name of Kubernetes Ingress. Name is combination of actual name of Ingress and kube-system name sapce id.
|
|
UID
|
Uid of Ingress. |
|
Namespace
|
Name space name where the Ingress belongs. |
|
Resource Version
|
In Kubernetes, resourceVersion is a unique identifier assigned to an API resource instance that changes every time the resource is modified. It helps track updates and ensures consistency when working with Kubernetes objects.
|
|
Creation Timestamp
|
The creationTimestamp field in a Kubernetes resource represents the exact time when the object was created. |
Interface Properties
The interface details display a list of interfaces for each device, including both physical and logical interfaces.

Neighbor Topology
NetBrain provides visibility and insights into your cloud network, including Kubernetes networking objects connectivity and topology, include:
-
IP connection topology between:
- Pod and Node
- Node and Node
- Pod and Pod
- Node and External Devices (F5/Router/Switch…)
-
Logic connection topology between:
- Pod and Service
- Node and Service
- Ingress and Service
-
L2 Overlay connection (VXLAN) topology between:
- Node and Node
- Node and External Devices (F5/Router/Switch…)
- Kubernetes Resource Hierarchy View Map:

- Kubernetes Cluster Hierarchy View Map:

- Kubernetes Flannel VXLAN View Map:

Data Tables
NetBrain provides insight into key Kubernetes data via Dynamic Maps, with the following data tables presented on the map:
|
Device Type
|
Data Table
|
Details
|
|---|---|---|
|
Kubernetes Node
|
Kubernetes Node Port Table
|
Details of Node Port services, including the assigned node ports and their mapped services.
|
|
Kubernetes Node Virtual Route Table
|
Logical route table computed by NetBrain to illustrate the intra-cluster traffic flow.
|
|
|
VXLAN Peer Table
|
Displays VXLAN peer details, including peer IP addresses overlay networking.
|
|
|
Kubernetes Service
|
Kubernetes Service Backend Table
|
Lists backend pods for a given service, including pod names, IP addresses, and service ports.
|
|
Kubernetes Node Virtual Route Table
|
Logical route table computed by NetBrain to illustrate the intra-cluster traffic flow.
|
|
|
Kubernetes Ingress
|
Kubernetes Ingress Rule Table
|
Display the mapping of Ingress URLs to backend services, detailing layer 7 routing rules for traffic distribution.
|
|
Kubernetes Node Virtual Route Table
|
Logical route table computed by NetBrain to illustrate the intra-cluster traffic flow.
|
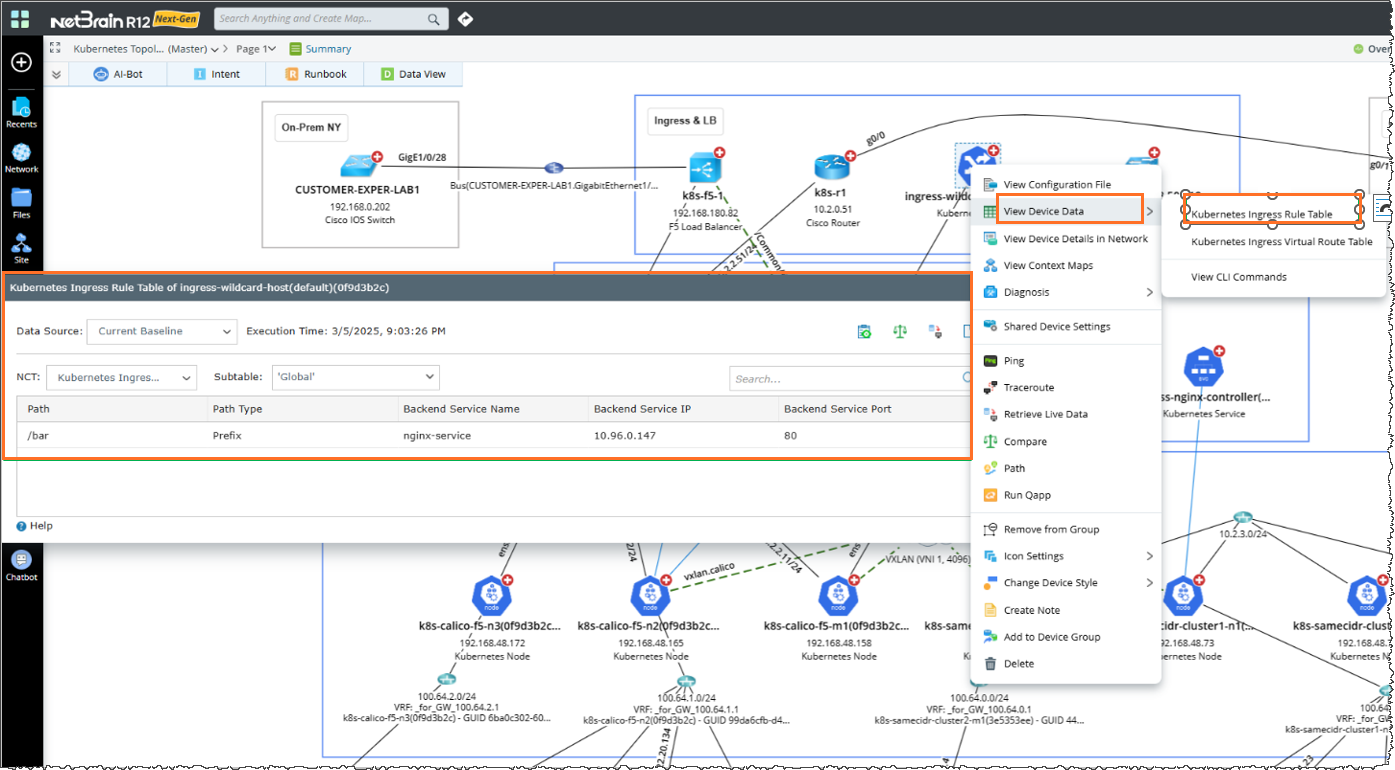
Data View Template
NetBrain provides visibility into key cloud network data on the Dynamic Map via Data View Template feature.

Calculate End-to-End Path
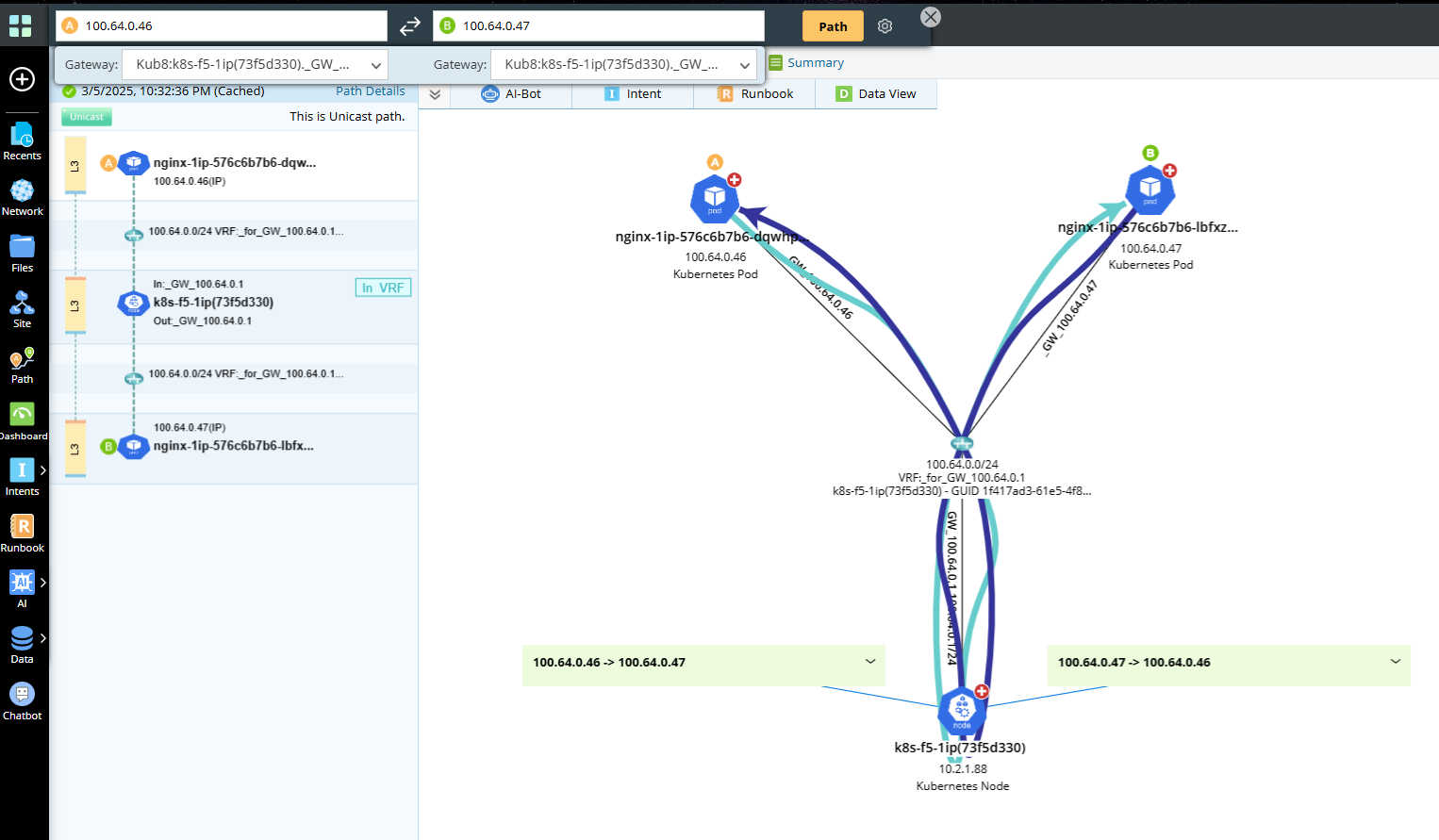
- Pod to Pod Traffic Path in same Node Calculated by IP Address
When traffic from one pod to another pod in same node, path calculated by IP address shown below.
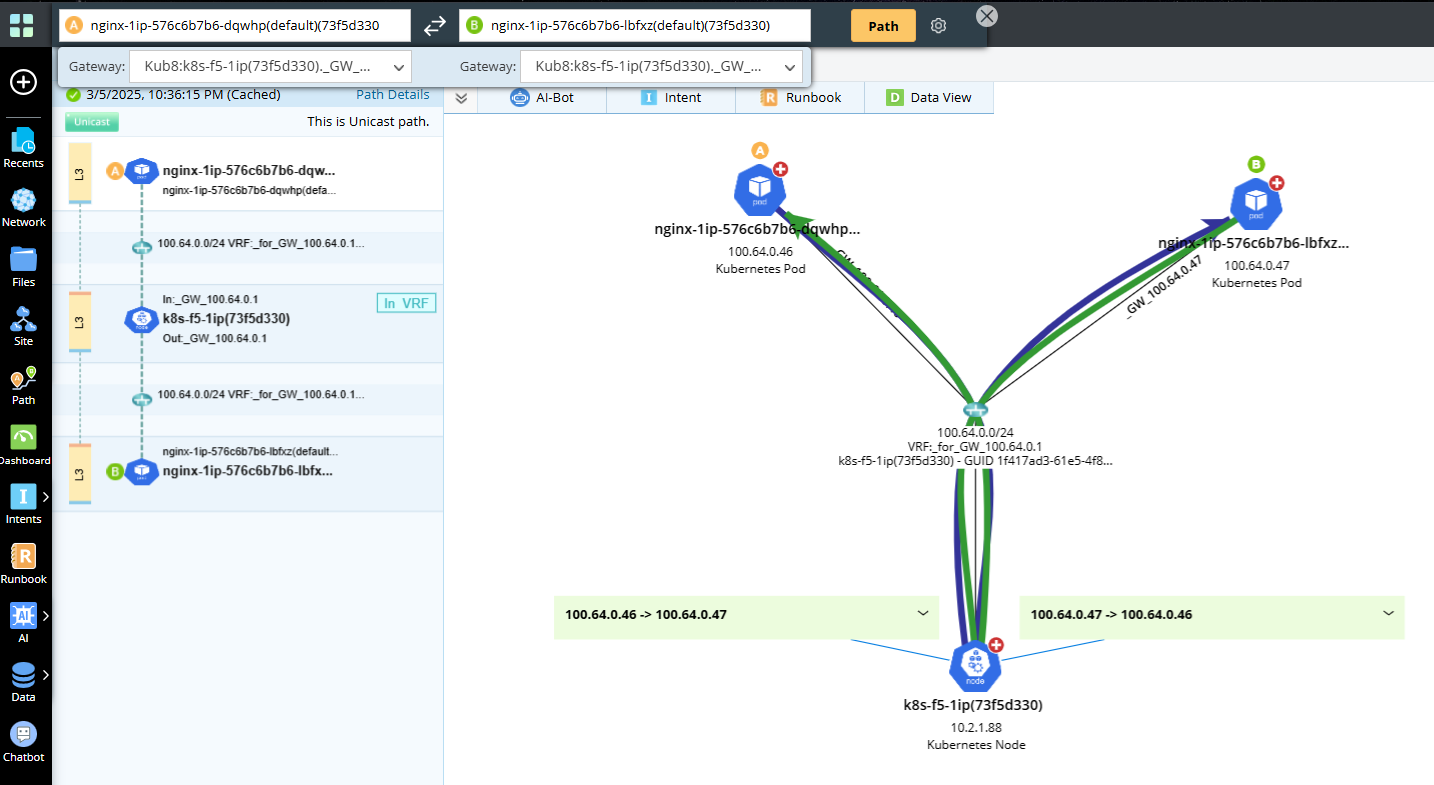
- Pod to Pod Traffic Path in same Node Calculated by Host Name
When traffic from one pod to another pod in same node, path calculated by Host Name shown below.
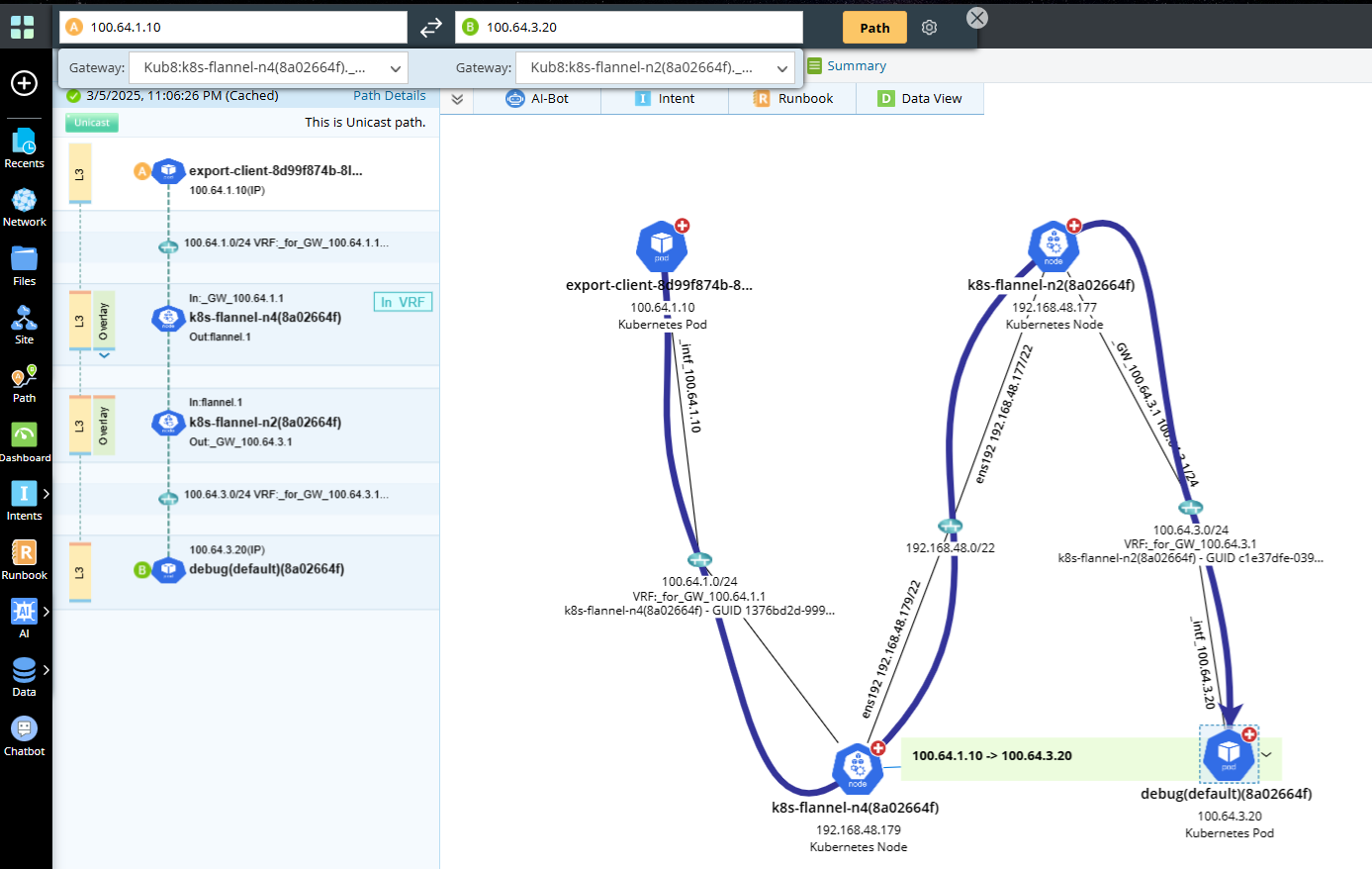
- Pod to Pod Traffic Path in Different Pod Calculated by IP Address/Host Name
When traffic from one pod to another pod in different node, path calculated by IP Address shown below.
- Pod to Service Traffic Path Calculated by IP + Port
When traffic from one pod to another pod in different node, path calculated by IP Address shown below.

- External to Node Port Service Traffic Path Calculated by Node IP + Port
When traffic from outside cluster to Node Port of Node, path calculated show as below.

- External to Load balance Service with F5 CIS Integration
When an F5 load balancer hosts a Load Balancer service, with pool members defined by Node IP and Node Port, the path calculation is outlined below.

Automate Observability
The NetBrain Automation Platform enables you to automate the diagnosis of your Kubernetes environment.

Supports basic intent-based automation use cases, like Configuration Drift Check, as a built-in solution. Automation can also be scaled to support a wide range of Kubernetes use cases. For more details, contact NetBrain Support.
Config Change Automation sample:
