Build Base Table via Device Interface
When to build ADT by selecting Interfaces of Device Group/Map?
ADT can be built via the Interfaces of Device Group/Map when certain device data/map data and interface data in pre-defined link groups within the domain are used to troubleshoot specific network issues. This enables the display of relevant data (e.g., the device interface) and the association of troubleshooting intents with the device interface.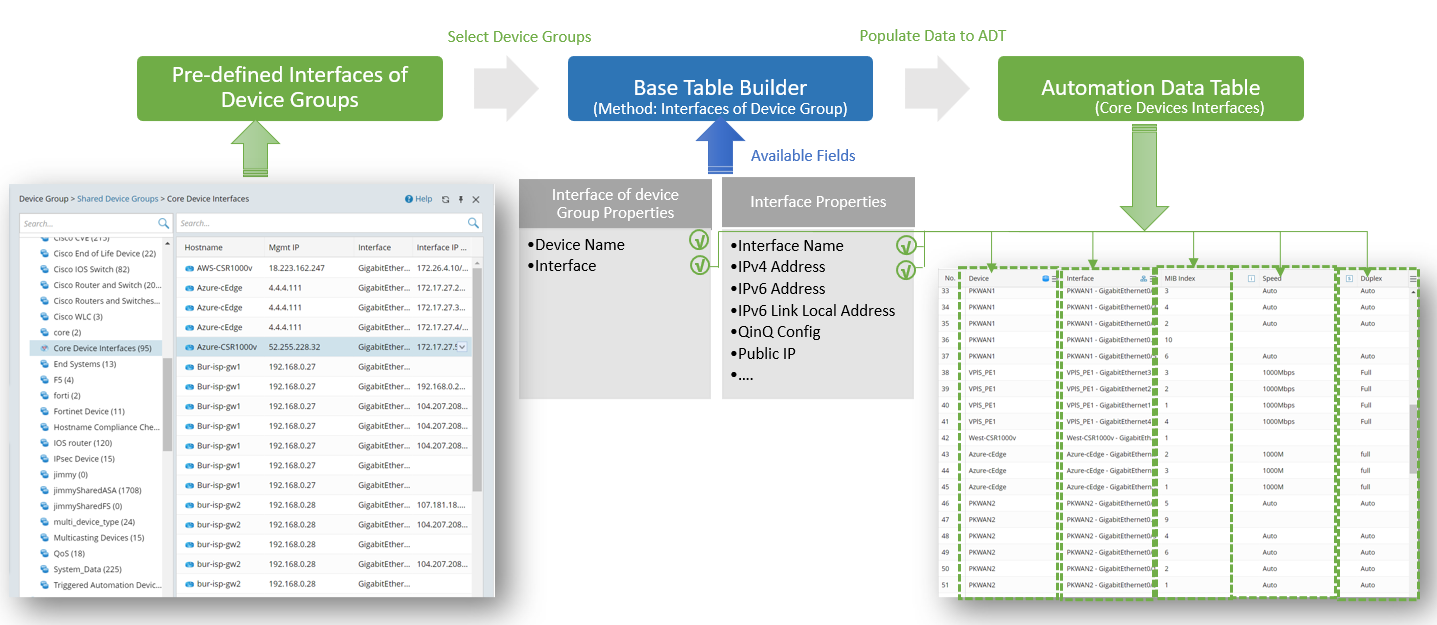
Define Base Table via Device Interface of Device Group
The interface of device group is used as an input, and the device, interface and interface properties will be used as input data for filling the table rows. Device and Interfaces can be used as built-in data.
Prerequisites: Create Device Groups containing devices with interface.
- Open Automation Data Table Manager, then create a new table (for example, WAN_Interface) and select location you wish to save the table.
- Click Table Builder to open Automation Data Table Builder of the created ADT.
- Under the Define Base Table tab of Table Builder, define the following settings:
- Select Method to Build Base Table: Select Device Interface > Device Interface in Device Group.
- Description: Input descriptions for the base table to describe its use and function.
- Device Interfaces by Device Group: Select the created device groups containing device interface properties for building the base table with the devices and Interfaces in the device group.

Note: Only link groups are displayed as options, while device groups without device interface are automatically excluded from the Select Device Groups dialog
- Mapping Available Fields to Column Group: Drag and drop the available fields (for instance, Device, Interface, etc) to the column group definition area to create ADT columns automatically.

Note: Interface is mandatory fields in this ADT. Other interface properties can be optional fields.
Note: The Interface column is set as the table key as marked by the icon .
. - Click Save to save the settings. But the table data will not be built.
- Click Save and Build and define the build table setting as per your preferences. The system will save all the settings and start building table data.
Define Base Table via Device Interface on Selected Map
The interface on map is used as an input, and the device, interface and interface properties will be used as input data for filling the table rows. Device Interfaces on a map can be used as built-in data.
Prerequisites: Create a map with device interface properties on it.
- Open Automation Data Table Manager, then create a new table and select location you wish to save the table.
- Click Table Builder to open Automation Data Table Builder of the created ADT.
- Under the Define Base Table tab of the Table Builder, define the following settings:
- Select Method to Build Base Table: Select Device Interface > Device Interface on Selected Map.
- Description: Input descriptions for the base table to describe its use and function.
- Select Interfaces by Map: Select the created Interfaces on map for building the base table with the devices and Interfaces on the map.

Note: You can select map one by one or select map folder to select all the maps in it.
- Mapping Available Fields to Column Group: Drag and drop the available fields (for instance, Device, Interface, and Interface Name) to the column group definition area to create ADT columns automatically.

Note: Interface is mandatory fields in this ADT. Other interface properties can be optional fields.
Note: The Interface column is set as the table key as marked by the icon .
. - Click Save to save the base table settings.
- Click Save and Build. The Build Table dialog appears, define the settings as per your preferences.