Pop-up API Stub
Pop-up API Stub is a way to integrate with maps and runbooks to collect network data or troubleshoot network issues in third-party systems. Users can directly define a pop-up API stub, use maps and runbooks by clicking a hyperlink in their third-party systems, without the need to predefine API tasks, and only a few scripts are required.
The general workflow to use Pop-up API Stub is as follows:
1.In a third-party system: Define Scripts to Generate a Hyperlink for NetBrain Pop-up API Stub.
2.Click the hyperlink to Define Pop-up API Stub, such as map and runbook settings.
Step 1: Define Scripts to Generate a Hyperlink for Pop-up API Stub
For a third-party system like ServiceNow, a hyperlink can be created to track an incident. You can write scripts in the third-party system to generate a hyperlink for NetBrain pop-up API stub.
A sample script is as follows (replace sample parameters with real instances):
import urllib.parse
data1={
'tenant': 'tenant_name‘,
'domain':'domain_name',
'vendor':'ServiceNow', # the vendor name of your third-party system
'device':'device_name', # the hostname of the problem device
'search':'device_to_search', # this parameter is optional
'interface':'interface_name', # one interface of the problem devices and it is required to extend neighbors from the interface
'source':’172.24.32.210‘, # the source of a path, only used for calculating a path
'destination':'172.24.31.125', # the destination of a path, only used for calculating a path
}
print('https://IP address of your NetBrain Domain/apimaplink.html?'+ urllib.parse.urlencode(data1))
Step 2: Define Pop-up API Stub
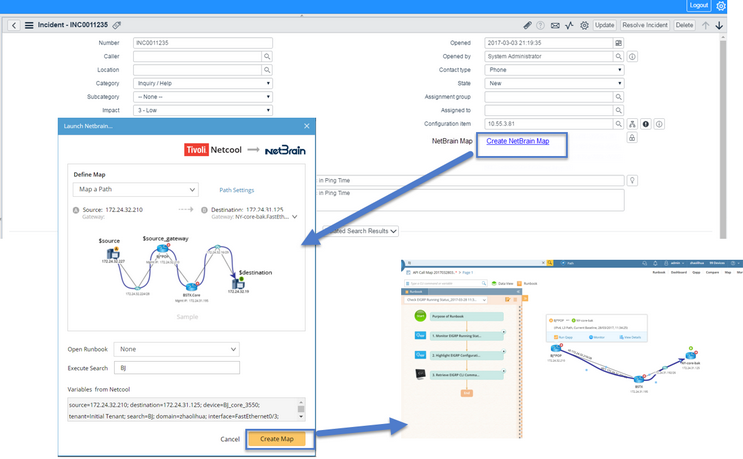
1.Click the generated hyperlink, and you will be required to log in to the NetBrain system. Then the Pop-up API Stub dialog prompts as follows, with the parameters defined in the scripts populated.

Tip: To have the vendor logo displayed at the upper-right corner, you need to manually add it to the system. See Adding an API Vendor for more details.
2.Select a way to create a map in the Define Map area. By default, the pop-up API stub creates a map as per the definitions in your scripts.
▪Map Device and its Neighbors — draw the problem device and its neighbors on a map. You need to specify the neighbor interfaces that you want to extend in the third-party system.
▪Map a Path — draw the traffic flow from a device to another. For a path, you can also define path parameters, such as data source, and protocol, by clicking the Path Settings hyperlink.
Note: You need to specify the destination and source devices when writing scripts in the third-party system.
▪Open Site Map of the Device — open the site where the problem device locates. To avoid changing the original site data, select the Make a copy of the Site Map checkbox.
▪Open Existing Map — open an existing map in your domain.
▪Open Context Map — open the context map of the problem device. Select a device category (Legacy Device or Cisco ACI Device) for the problem device.
▪New Empty Map — create a map page without any devices on it.
3.In the Open Runbook field, select a runbook to be executed on the map.
Tip: You can predefine your preferred runbooks for a third-party vendor in the System. See Adding an API Vendor for more details.
4.Select whether to search for devices. See Searching for Devices for more details.

