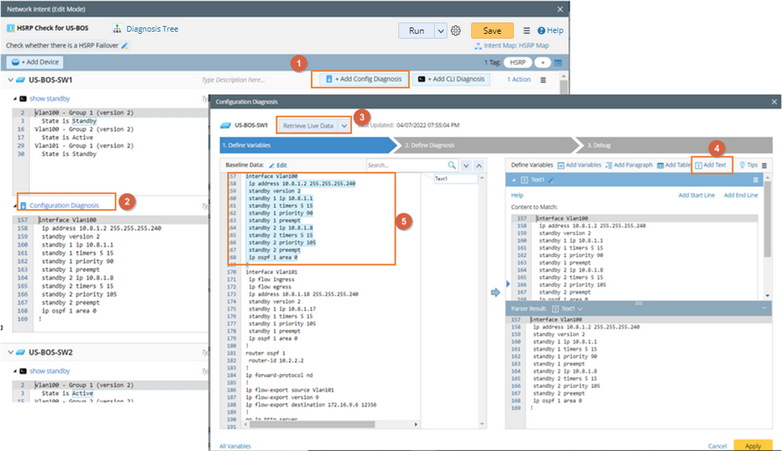
Defining Network Intent
Unlike Qapp, which defines diagnosis logic as a template and tries to run it on all devices across different customers’ network, NI is defined on the specific target devices of a particular network.
Complete the following steps to define a Network Intent.
1.Click the ![]() icon and select New Network Intent.
icon and select New Network Intent.
2.Enter an NI name and add the following components.
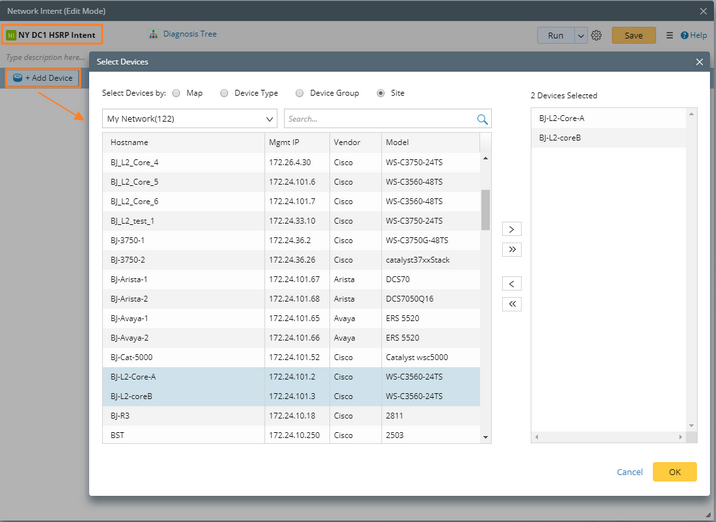
1)Click Add Device to add the target devices. In this case, devices are added by site. You can also add by map, device type, or device group.
2)Click Add Config Diagnosis and Add CLI Diagnosis to add the Config and CLI commands related to this NI. See adding config and CLI commands to NI for more details
3)Define parser for Config and CLI commands. See defining multiple types variables via visual parser for more details.
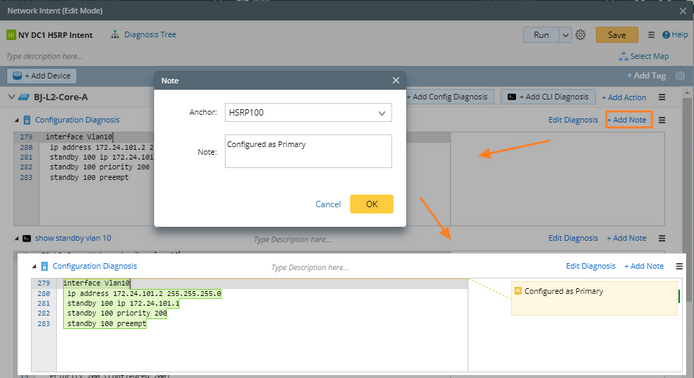
4)Add note,diagnosis and status code to this NI.
3.(Optional) Click the  icon and select Duplicate Section to duplicate the variables and diagnosis defined under the current device to another device.
icon and select Duplicate Section to duplicate the variables and diagnosis defined under the current device to another device.
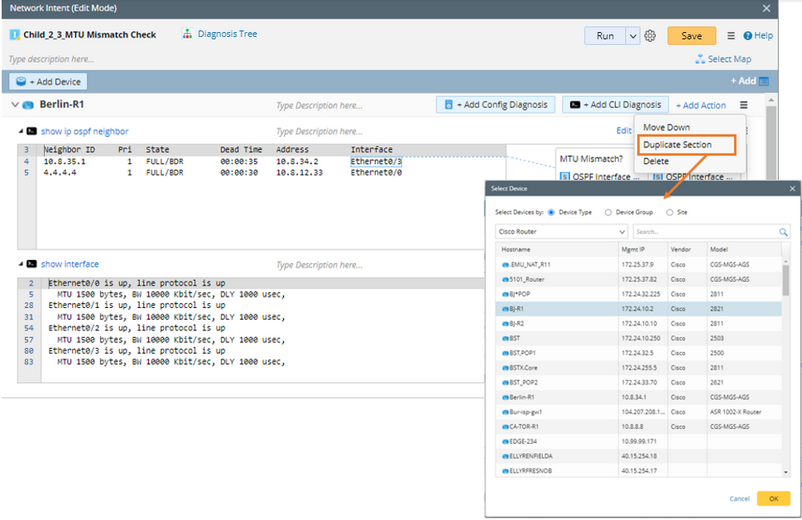
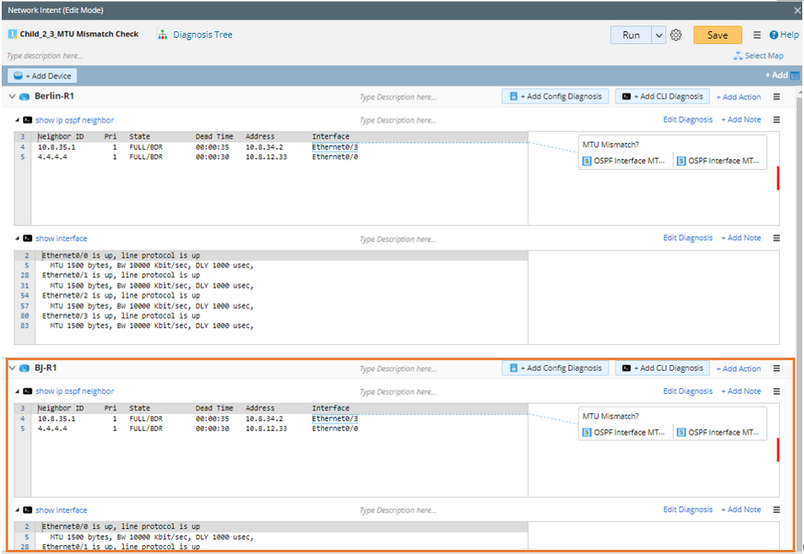
After selecting the devices, the variables and diagnosis under the current device Berlin-R1 will be duplicated to the selected devices.
4.Debug an NI step by step and check each step's input and output value.
5.(Optional) Click Select Map to associate the Network intent with a Reference Map to better express network problems.

When associating with a Reference Map, you have 2 options:
A.Reference to a copy of the current map in function map folder (Default option): this option will create a copy of the selected reference map, and the path will be associated with the copy of the map. You own the Editing Rights of the copy of the map.
B.Reference to the current map: this option will directly associate the path to an existing map. You may only have View Only privilege of the reference map.
6.(Optional) When using a sample NI, click the  icon and select Switch Devices to switch the devices in sample NI to the user’s real network devices. This will switch the devices in diagnosis, compound variable, compound table and Formula Column, as well as the baseline data.
icon and select Switch Devices to switch the devices in sample NI to the user’s real network devices. This will switch the devices in diagnosis, compound variable, compound table and Formula Column, as well as the baseline data.