Advanced Search
Advanced search allows you to build complex search queries to search for devices by using multiple search criteria and a boolean expression.
Using Advanced Search
1.Click the search bar and then select Advanced Search from the drop-down list.
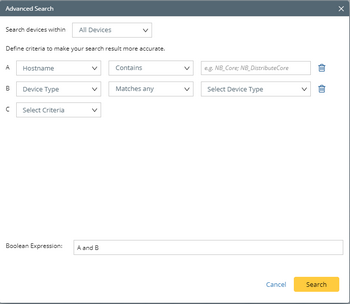
2.Specify the scope to search for devices.
3.Set search criteria A based on your needs:
1)Select a data source and a property from the first drop-down menu.
2)Select an operator from the second drop-down menu.
3)Specify the value of the property that you selected.
4)Repeat to set more conditions if required.
4.Define the condition combination in the Boolean Expression field. For example, A and B.
Note: When you select Hostname as data source from the first drop-down list, the system support the Hostname Matches + regular expressions. See Regex Search for more details.
Note: When you select Config File as data source, and Matches as the operator, the system supports "Matches Near", to better match two keywords separated by other words.
5. Click Search. The searched result is displayed as follows:

Components for Advanced Search
The following table lists the available components in an advanced search.
Component |
Description |
Option Values |
Search Scope |
The scope of devices. |
▪All Devices — all devices in the current domain. ▪Site — devices in one or more sites. ▪Device Group — devices in one or more device groups. |
Search Criteria |
Property |
▪Device Property — use one or more device properties to find devices. ▪Interface Property — use one or more interface properties to find devices. ▪Module Property — use one or more module properties to find devices. ▪Config File — use texts in the configuration file to find devices. ▪Front Server — use a Front Server to find their managed devices. |
Match Operator |
Specify multiple values by separating them with a semicolon (;). ▪Matches/Matches any/Does not match/Does not Match any — The full-text search pattern will be applied. ▪Contains/Does not contain — The * and ? characters are treated as either wildcards (only for a single term) or separators. |
|
Boolean Expression |
The logical relationships among search criteria. |
▪Capitalized letters to represent the search criteria (A, B, C ....). ▪Boolean operator (and/or), which is used to define the logical relationships among the search criteria. By default, the and operator is used. ▪Parentheses, which is used to combine some search criteria. |
