R12 Publication-2025July16
Text Replacement
Text replacement is a flexible way to automate text pre-processing before it can be parsed as expected. When you want to search and replace any string in the raw text, you can define a text replacement.
Text replacement can be defined at two levels:
- Format level: search and replace a string in the whole range of sample text in one format.
- Pattern level: In one format, you can define several patterns. Text replacement can be defined for one pattern. The system will search and replace a string in the given range of text that has been matched by a specific Parser’s definition in this pattern.
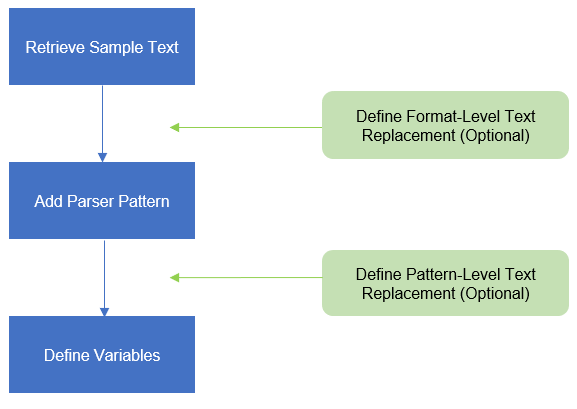
Text Replacement Entrance
When defining a text replacement, you can add one or multiple replacement rules from the following two entrances.
- You can define format-level text replacement from the following entrance: Click Define Replacement from the format drop-down menu, then define the search and replacement rules in the pop-up window.
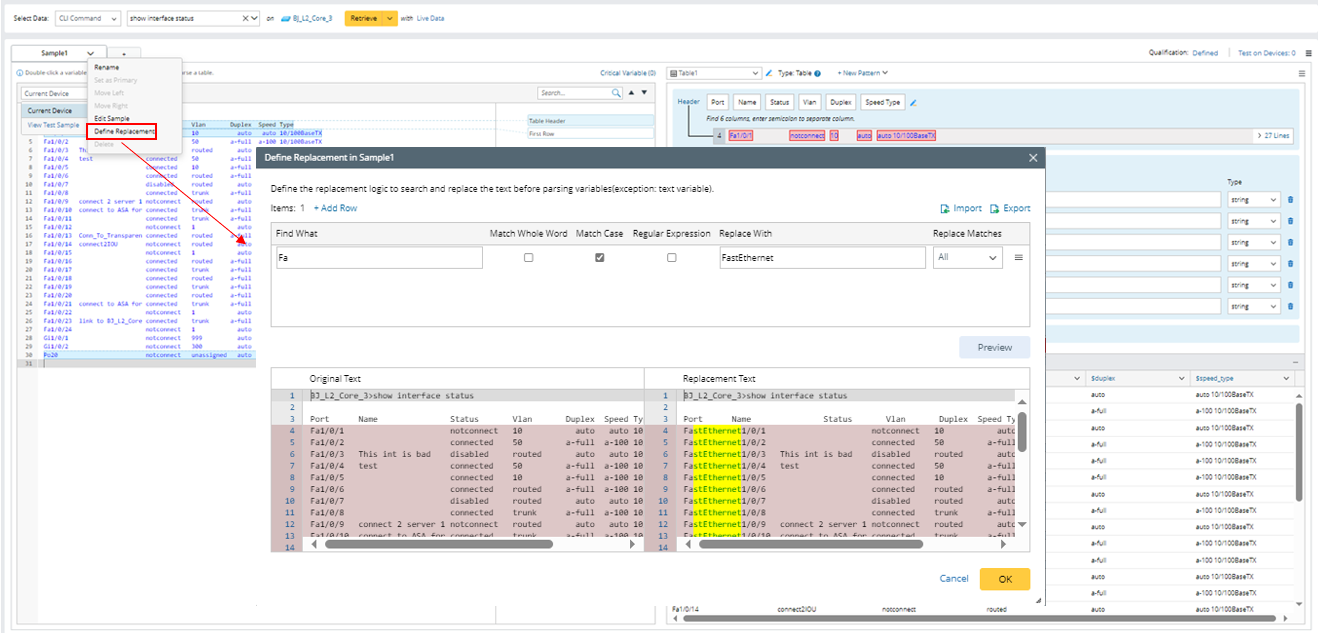
- You can define pattern-level text replacement from the following entrance: Click Define Replacement from the pattern drop-down menu, then define the search and replacement rules in the pop-up window.
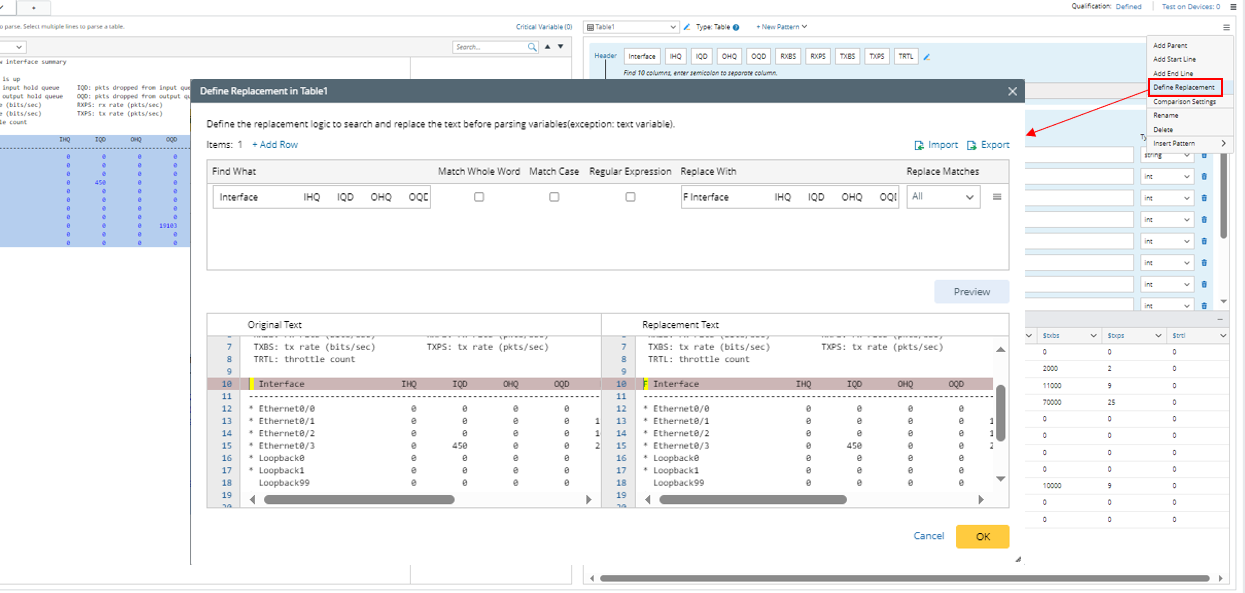
 | Note: The settings and logics for defining text replacement from the two entrances are the same. |
Use Cases of Text Replacement
- Form a Table Header Line
When a device command output looks similar to a standard table format but only misses a table header line, you can define text replacement to replace the line of text ahead of the table data with a customized table header line. This twist allows you to continue to define a Table Parser to parse the table data. - Fill Up Table Headers
When one or more table headers are missing in the sample text, using a Table Parser directly will lose the data of those columns. - Rename Duplicate Table Header
When there are two table headers with a duplicate name, the latter one cannot be parsed. As a workaround, rename table headers, so each header has a unique name. This can be done by replacing the line of table headers with a new one. - Adjust table column width
Sometimes the table headers are not aligned with data cells and cannot be parsed by a Table Parser. For example, the alignment gap between table headers and cells causes an incorrect parsed result. - Translate Interface Name
Sometimes interface names in the raw text are irregular and cannot be further used before manual processing.
The following is an example of searching and replacing interface name with a full interface name.
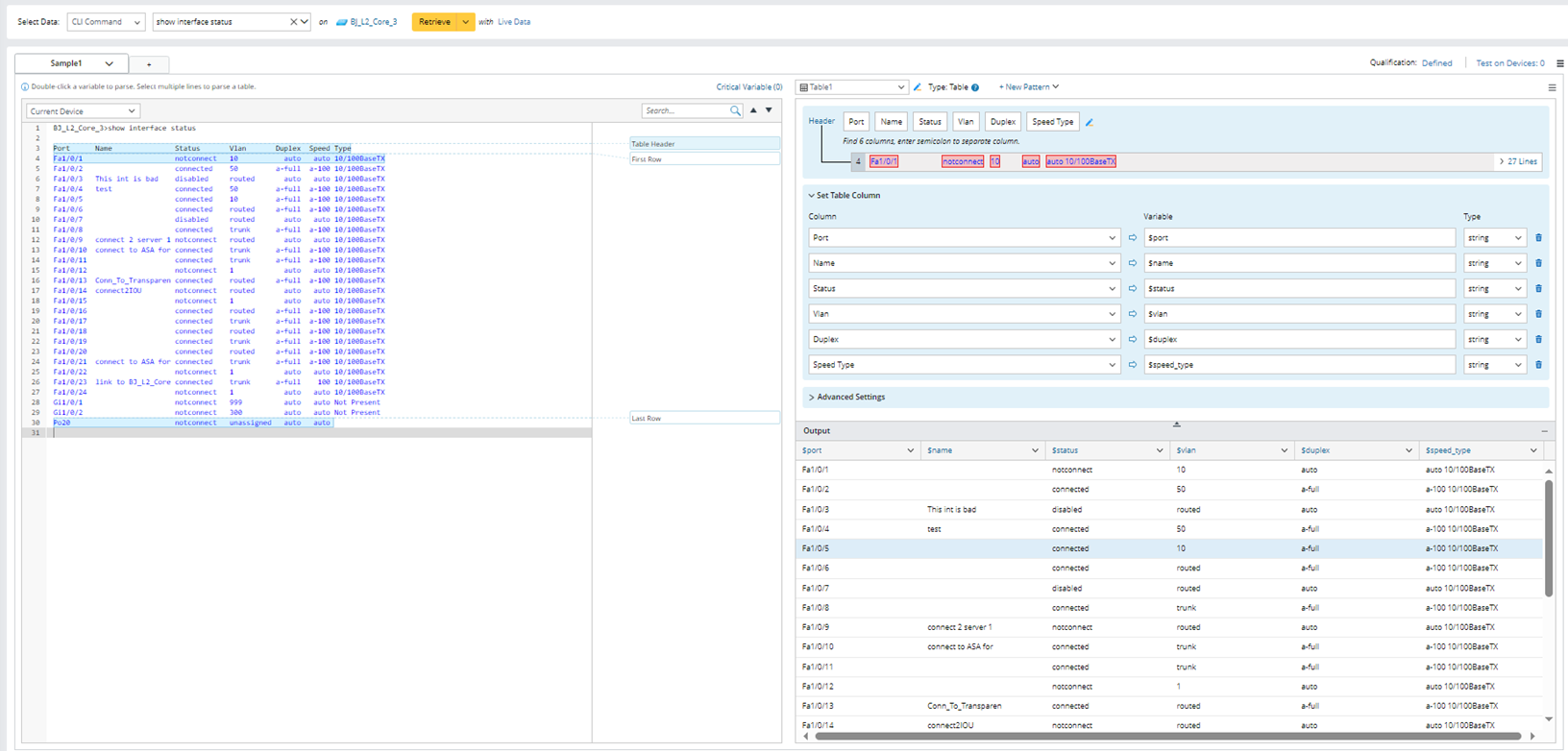
- Retrieve command data “show interface status” on the device BJ_L2_Core_3, then select several lines from the sample text to parser table. The interface name is short name in the parsed results.
- Click Define Replacement from the Format menu.
- In the pop-up window, define the settings to change the short name (Fa) to long name (FastEthernet).
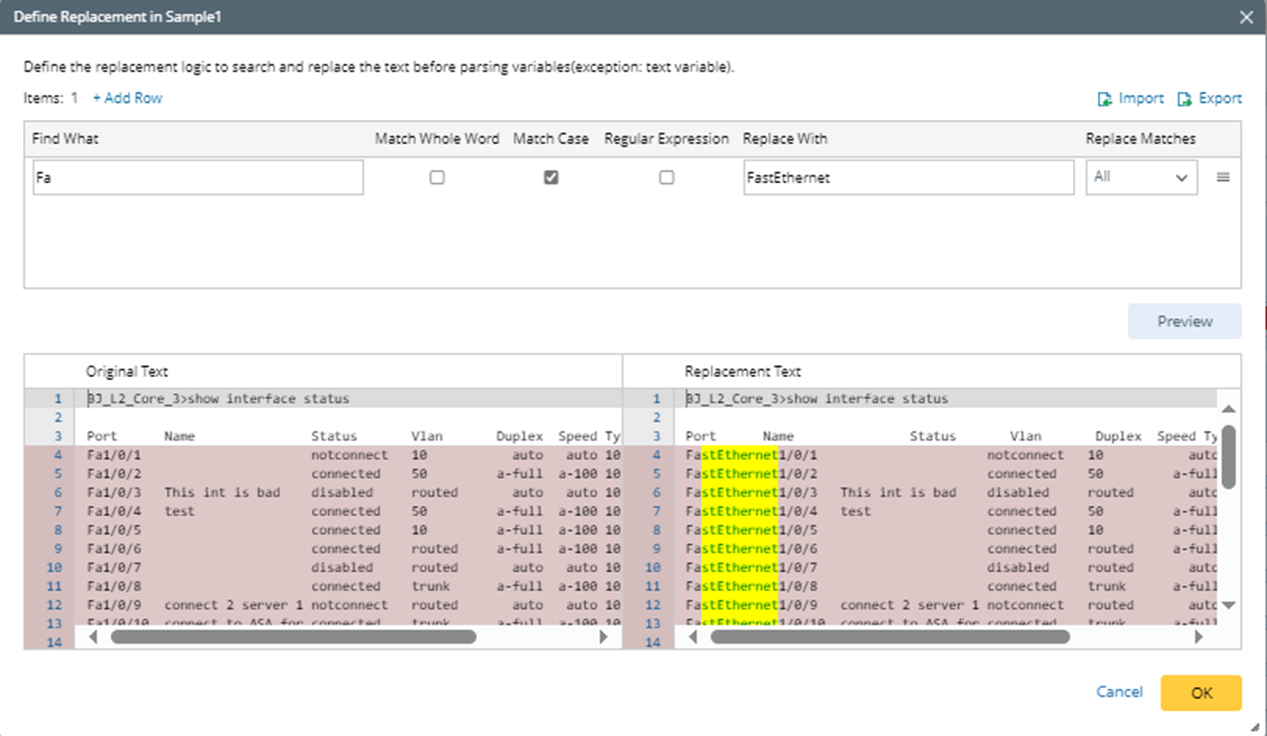
- Click +Add Row, then set to replace Fa with FastEthernet. The meanings of the options are described below:
- Find What - the text you are searching for in the given range.
- Match Whole Word - once enabled, searches will only match if the result is a whole word, e.g., a search for “FastEthernet” will not return “FastEthernet1/2”.
- Match Case - once enabled, search terms are case-sensitive, e.g., a search for “ethernet” will not return “Ethernet”.
- Regular Expression - once enabled, search terms will use the regular expression engine to find complex patterns in the text; otherwise, search terms will be interpreted literally.
- Replace With - the text that will replace what is matched.
- Replace All Matches - replace all matches in the text scope.
- Replace First Only - replace the first match only.
- Find What - the text you are searching for in the given range.
- Click Preview, you can preview the changes in the lower part of this window.
- Click OK to close this window, then you can see the changed results in the output area.
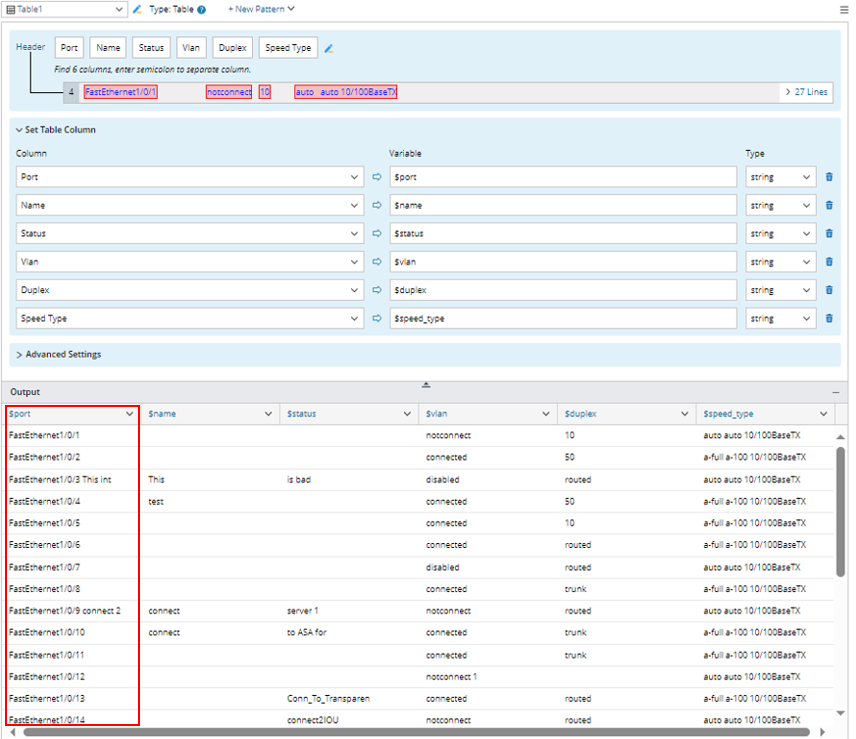
- Click +Add Row, then set to replace Fa with FastEthernet. The meanings of the options are described below: