PBTF Use Flow
PBTF is designed to help you troubleshoot application-related issues. You can do both Interactive Troubleshooting and Triggered Automation with PBTF.
Path-based Interactive Troubleshooting
- Discover and Document the Path when the network is healthy.
- Use path to interactively troubleshoot network issues
Discover and Document the Path when the network is healthy
- Define and discover the path (When Network is Healthy)
When you troubleshoot the network issues, your network may not be healthy, and the path may fail. Knowing the path when the network is healthy can speed up troubleshooting. Therefore, you should identify the critical applications, define the path source/destination and their gateway, and discover these paths when the network is healthy.
You can use Path Browser to define the path and Path IP and Fix-up Gateway to define the gateways. Or you can directly map the A/B path and save the path in the Path Browser.
You can document the calculated paths and related path logic, including:
- Set Path Description
- Enter Path Note on each hop device to enter the related network design and troubleshooting knowledge.
- Select Path Reference Map that contains not only path results but also design notes or related config-let, failover annotation, etc. See more details for the Reference map.
- Set a historical Path as the Golden Path, which should be the best traffic path as designed.
- Define Path NI (When Network is Healthy)
You can also define a Path NI to document the path diagnosis logic when the network is healthy and associate it with the path. NI is the automation specific to a device or a set of devices with its local baseline data. When you define NI for a path, all hop devices of the path will be put into NI. The path NI can diagnose slow application issues or other path issues, for example,
- Checking L3 failover (the next hop changes).
- Monitoring utilization (QoS drop, CPU/memory high, link error, etc.)
- Checking configuration consistency (QoS, MTU, etc.)
See more details for Path NI.
Use path to interactively troubleshoot network issues
- Find Pre-documented Path and Review Path Documents (During troubleshooting)
When you enter the source and destination in the A/B path UI, the documented path with the same source/destination will be displayed. You can select one path to view its results on the map, including the path description, note, path reference map, and Path logic - Drill-down analysis: calculate live Path and Compare with Cached Path (During troubleshooting)
During troubleshooting, you can discover the path from the live network (the live path) and compare it with the cached path.- Select golden or cached Path Results to draw it on the map.
- Calculate Live Path and compare it with golden Path or cached Path
- Select golden or cached Path Results to draw it on the map.
- Drill-down analysis - Execute Path intent (During troubleshooting)
You can browse alert summary messages in the Incident pane created by Trigger Diagnosis and open the corresponding path NI to view the detailed diagnosis alerts. You can also run a Path NI to check the newest diagnosis results.
Path-based Triggered Automation Use Case
- Discover the Path
- Document the Path (When Network is Healthy)
- Define the Path NI (When Network is Healthy)
- Install Path-based Trigger Automation (When Network is Healthy)
The Path NI can be triggered by TAF or Preventive Automation Framework. To install the Path NI for triggered automation, you need to:- Add tags to the Path NI. Recommend using tags that include the path source/destination IP, DNS name, application name, or path name to make it easy for Triggered Diagnosis to match the right NI.
- Add all Path NIs into a NIC as static member NIs.
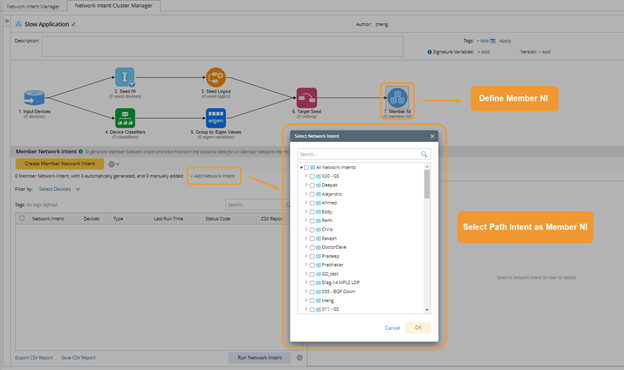
- Define trigger diagnosis using the NIC and define the NIC filter condition with path NI tags.
- Add tags to the Path NI. Recommend using tags that include the path source/destination IP, DNS name, application name, or path name to make it easy for Triggered Diagnosis to match the right NI.
- Open NetworkBrain Incident from ServiceNow Ticket (During troubleshooting)
A NetworkBrain incident can be created automatically for A ServiceNow ticket based on the TAF definition. You can open the ServiceNow app, check the ticket, and find the related link to the NetworkBrain Incident.
- Find documented Path and Review Path Documents (During troubleshooting)
If a path map is saved as a NI reference map (See more details on Defining Network Intent), a message containing a hyperlink to the path map will be displayed in the incident pane after the NI is triggered. You can open the Path map, locate the path from the map and view the path description, path note, path reference map, and Path logic.
- Review Trigger Diagnosis Result (During troubleshooting)
You can review the Path NI Definition to understand the trigger diagnosis result. - Drill-down analysis - Calculate live Path and Compare with Cached Path (During troubleshooting)
- Drill-down analysis - Execute Path intent (During troubleshooting)