Types of Diagnosis Logic
When you add a diagnosis to a NI, you can define various diagnosis logic to make the NI more flexible and verify the network design more accurately.
Table/Paragraph/Collector Variable
A variable can be a single variable such as $state or a table (paragraph, collector). For the table/paragraph/collector variable, you can select the Loop Table Rows for the system to loop through each table's row. Take the OSPF neighbor table as an example. There are seven lines of neighbor information in the CLI result (the blue rows on the left). The diagnosis execution will determine whether the state contains full line by line (7 lines in total).
Different Variable Types
Different types of variables have various operations such as Equals, Does not equal, Contains, etc. Compound variables and compound tables can be used in diagnosis definition as well.
| Variable Type | Example |
| String |  |
| Int/Float | 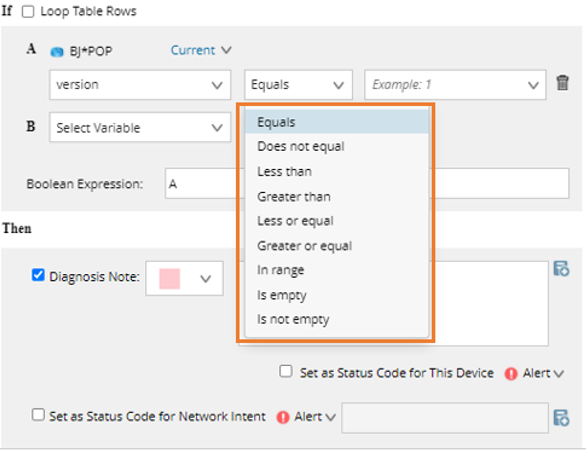 |
Different Data Source
For each variable defined in the diagnosis, you can select its data sources: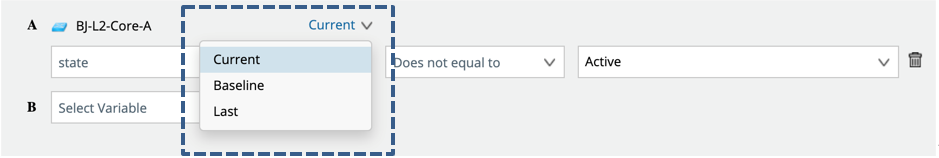
- Current: the value of this execution result of the NI .
- Baseline: the baseline data.
- Last: the NI will be executed twice and compare the current data with the last data.
The following diagnosis compares the current state with the baseline state:
The following diagnosis compares the current CRC value with the last CRC value:
Check Device Pair
You can compare the variables from the different devices. The following compares MTU from two neighbor devices.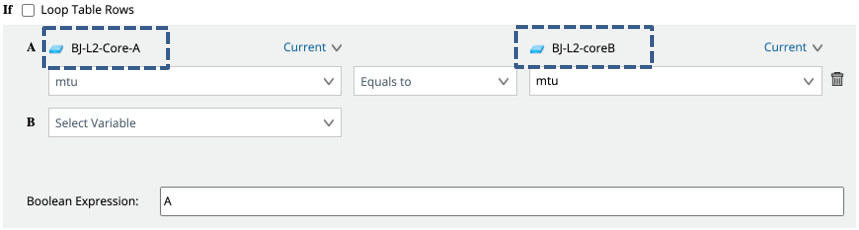
Use Compound Condition
You can have multiple simple conditions and combine them into a Boolean expression (and/or).