2023-Nov-03-R11.1a
Text Replacement
Text replacement is a flexible way to automate text pre-processing before it can be parsed as expected. When you want to search and replace any string in the raw text, you can define a text replacement.

|
Note: Text replacement is unavailable to Text Parser and cannot be applied to retrieved sample text. |
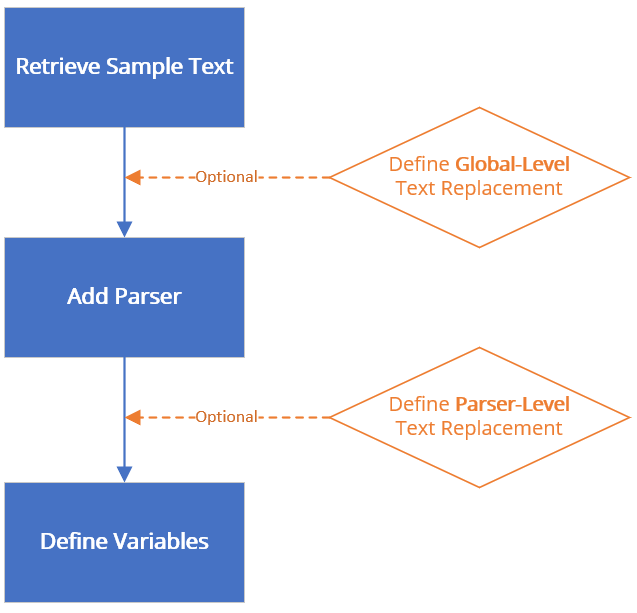
Text replacement can be defined in two levels:
- Global level: search and replace a string in the whole range of sample text.
- Parser level: search and replace a string in the given range of text that has been matched by a specific Parser’s definition.
Text Replacement Rules
When defining a text replacement, you can add multiple replacement rules. Each rule contains two objects as follows.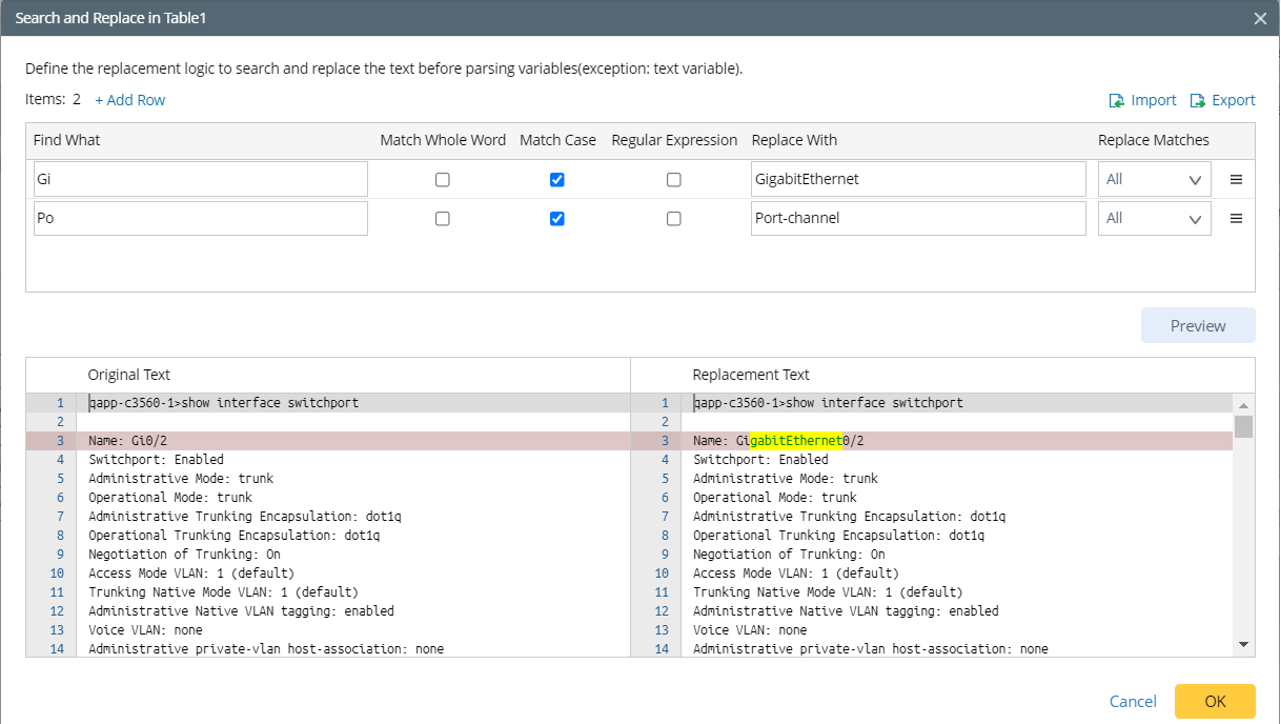
- Find What - the text you are searching for in the given range.
- Match Whole Word - once enabled, searches will only match if the result is a whole word, e.g., a search for “FastEthernet” will not return “FastEthernet1/2”.
- Match Case - once enabled, search terms are case-sensitive, e.g., a search for “ethernet” will not return “Ethernet”.
- Regular Expression - once enabled, search terms will use the regular expression engine to find complex patterns in the text; otherwise, search terms will be interpreted literally.
- Replace With - the text that will replace what is matched.
- Replace All Matches - replace all matches in the text scope.
- Replace First Only - replace the first match only.
Use Cases of Text Replacement
- Form a Table Header Line
When a device command output looks similar to a standard table format but only misses a table header line, you can define text replacement to replace the line of text ahead of the table data with a customized table header line. This twist allows you to continue to define a Table Parser to parse the table data. - Fill Up Table Headers
When one or more table headers are missing in the sample text, using a Table Parser directly will lose the data of those columns. - Rename Duplicate Table Header
When there are two table headers with a duplicate name, the latter one cannot be parsed. As a workaround, rename table headers, so each header has a unique name. This can be done by replacing the line of table headers with a new one. - Adjust table column width
Sometimes the table headers are not aligned with data cells and cannot be parsed by a Table Parser. For example, the alignment gap between table headers and cells causes an incorrect parsed result. - Translate Interface Name
Sometimes interface names in the raw text are irregular and cannot be further used before manual processing.