Support Native Objects
In some scenarios, users may want to perform diagnoses on specific objects. For example, build a diagnosis and generate output based on data from the device (‘$device’ object), not just the current device (‘$this_device’). NI supports the native objects in NI: device, interface, map, path, site, device group, and file. Each type of object has a set of property variables and methods.
Sample Use Cases:
-
For Device Object:
- Use Case 1: Loop a device group/site and return the $device object, then use the associated GDR/NCT for programming. Then users can also draw $devices to map and highlight the $devices’ properties.
- Use Case 2: Create a diagnosis and find a device list that meets the requirements in the domain, then loop this device list to call follow-up NIT. Finally, draw devices to map and highlight the devices with alert/success.
-
For Map Object:
- Use Case 1: Support looping map objects via map folders (level 1 only) and looping each device within the map.
- Use Case 2: Schedule to update a map via intent. For example, draw a multicast tree map and show the required data on this map.
-
For Site Object:
- Users can use intent to add devices to a site.
-
For Device Group Object:
- Users can use intent to create device groups or add devices to a device group.
-
For File Object:
- Use a simple text file, which includes a set of IP strings of critical servers in a company server farm (e.g. 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.2, ...), then use this IP list to do network change verification - Ping all these IPs from a set of key devices.
Property Variables and Methods
The following table lists the supported native objects.
| Object Type | Properties | ID Property | Methods | Related Functions & Diagnosis Actions | ||
| Device |
|
|
|
Related Global Functions:
Related Diagnosis Actions:
|
||
| Interface |
|
|
|
Interface can be used in the return value of the following functions:
Related Global Functions:
Related Diagnosis Logics:
|
||
| Path |
|
|
|
Related Global Functions:
Related Diagnosis Logics:
|
||
| Map |
|
|
|
Related Global Functions:
Note: Only common maps are supported in the above functions; function maps are not supported. Related Diagnosis Logics:
|
||
| Site |
|
|
|
Related Global Functions:
Related Diagnosis Logics:
|
||
| DeviceGroup |
|
|
|
Related Global Functions:
Related Diagnosis Logics:
|
||
| File |
|
|
|
Related Global Functions:
Related Diagnosis Logics:
|
For the parameters 'TopologyType' and 'InterfaceType' mentioned in the above Method column, you can input either a number or a string (enclosed in double quotes). It is recommended to use a string for better readability of the intent logic.
|
Parameter
|
Candidate Value
|
Related Object Methods
|
|---|---|---|
|
TopologyType
|
"L2 Topology" = 1
"IPv4 L3 Topology" = 2
"IPv6 L3 Topology" = 3
"L3 VPN Tunnel" = 4
"Logical Topology" = 5
"L2 Overlay Topology" = 6
|
Device: GetTopoNeighbors
Interface: GetTopoNeighbors
|
|
InterfaceType
|
"Interface" = 1
"IPv4 Interface" = 2
"IPv6 Interface" = 3
"IPsec VPN Interface" = 4
"GRE VPN Interface" = 5
|
Device: GetInterfaceList
Device: GetInterfaceNameList
|
Related Global Functions
See Supported Built-in Functions in Network Intent for more details.

|
Note:
|
Find object in Domain
You can use a diagnosis logic to find various types of objects in the domain. The found objects that meet the conditions will be placed in a specified result list.
-
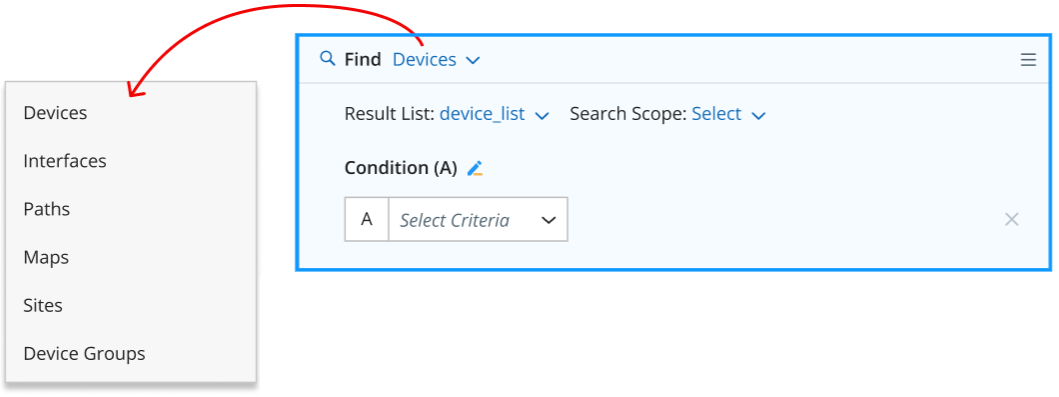
You can select one of the following 6 object types, and the ‘Find’ UI will change depending on the selected object type.
-
For ‘Result List’, you can directly select a list variable in global variables or local variables, whose variable type should be consistent with the selected object.
You can also define a new list variable by clicking Define Variable. The variable type is fixed, and you only need to enter the list variable name and specify whether it is a local variable or a global variable.

After the above definition, all matching objects found according to the specified scope and condition will be put into a specified result list variable. If no condition is defined, all objects in the scope will be added to the list.
Depending on the selected object type, the UI is displayed as follows:
-
Find Devices in Domain: You can find devices from a device group, site, map, or domain, and then define the criteria to narrow down the scope.

$this_device can be used as a special device object so users can use the device property variable directly.

-
Find Interfaces in Domain: You can find interfaces from a device group, map, or domain, then define the criteria related to the device and interface to narrow down the scope.

-
Find Paths in Domain: The search scope is domain by default. You can search path from all application paths in a domain.

-
Find Maps in Folder: You just need to select a map folder as the search scope, then define the criteria to narrow down the scope.

-
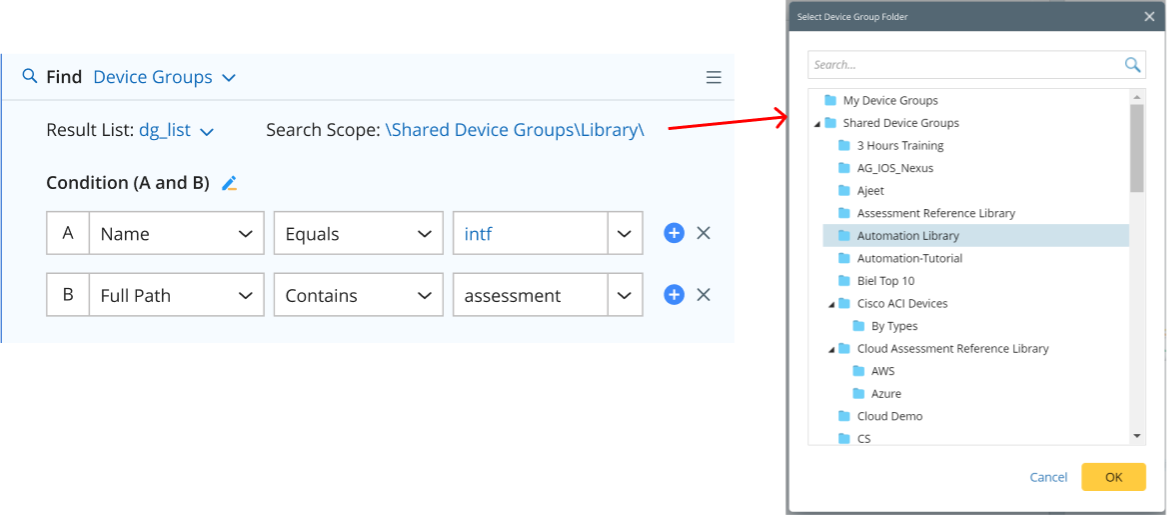
Find Device Groups in Folder: You just need to select a device group folder as the search scope, then define the criteria to narrow down the scope.
-
Find Sites in Domain: There is no need to specify the search scope, and the sites will be searched in all container/leaf sites of the current domain.
