Azure Route Server Support
Azure Route Server allows you to manage network infrastructure. It provides visibility into nodes, topology, data tables, and end-to-end (E2E) paths, enabling administrators to monitor components, understand system structure, access organized data, and optimize data flow for improved efficiency and performance.
Discover Azure Route Server
NetBrain supports the discovery of the cloud network, including the Azure Route Server node.
To enable this, configure the appropriate Azure IAM permissions and set up the API server by following the NetBrain Azure Quick Setup Guide.

|
Note: To support the Azure Route Server feature, the following IAM permissions must be added for the NetBrain API server:
Refer to: NetBrain Required Azure IAM permissions |
Once configured, initiate network discovery to detect all cloud components, including the Azure Route Server node, as shown below.
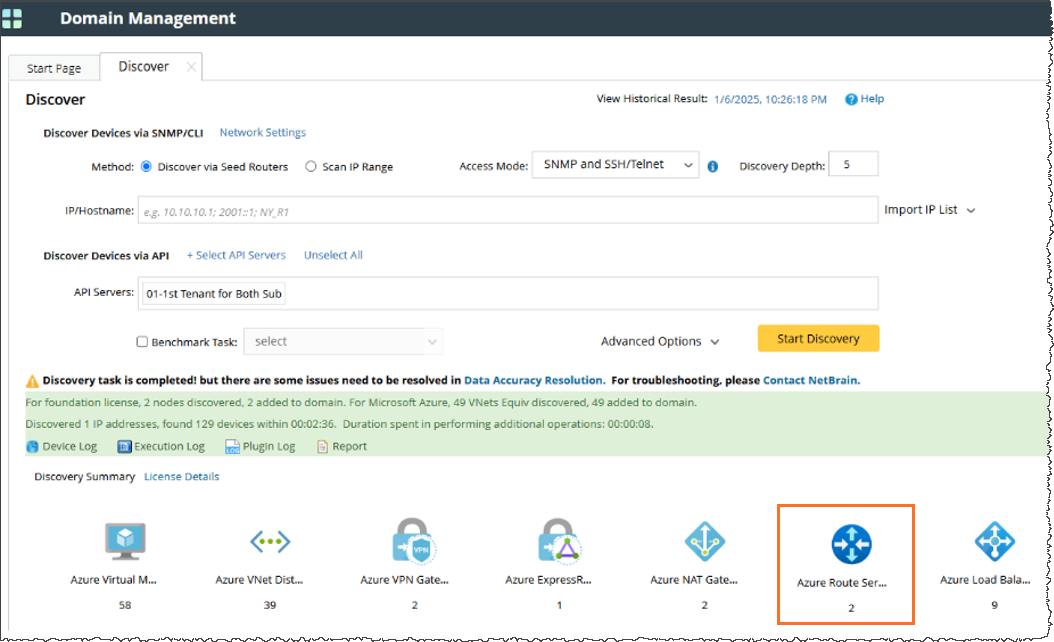
Feature Scope
The following are the feature scope in the Azure Route Server:
- Network Tree
- Context Map
- Device Details
- Neighbor Topology
- Data Table
- End-to-End Path
- Branch-to-Branch Traffic Path
- Routing Preference: ExpressRoute
- Routing Preference: VPN
- Routing Preference: AS Path
Feature Usage
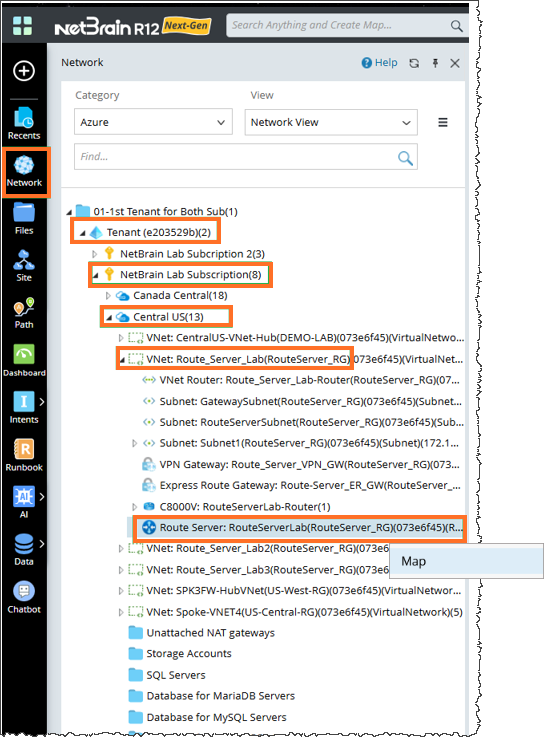
- Network Tree: Locate the Azure Route Server node from Network Tree. The Network Tree provides a structured view, making it easy to locate specific nodes and understand the resource hierarchy within your cloud environment. The hierarchy follows this order: Tenant > Subscription > Region > VNet > Azure Route Server. Right-click the Route Server and open the Map.
- Contex Map and Device Details: Right-click the node on the map and select View the Context Map. This will display the Context Map, which provides information about Azure Route Server neighbor connectivity and Device Details, including basic information about Azure Route Server. The interface also includes a hyperlink to access the original data in the Azure Portal.
Context Map: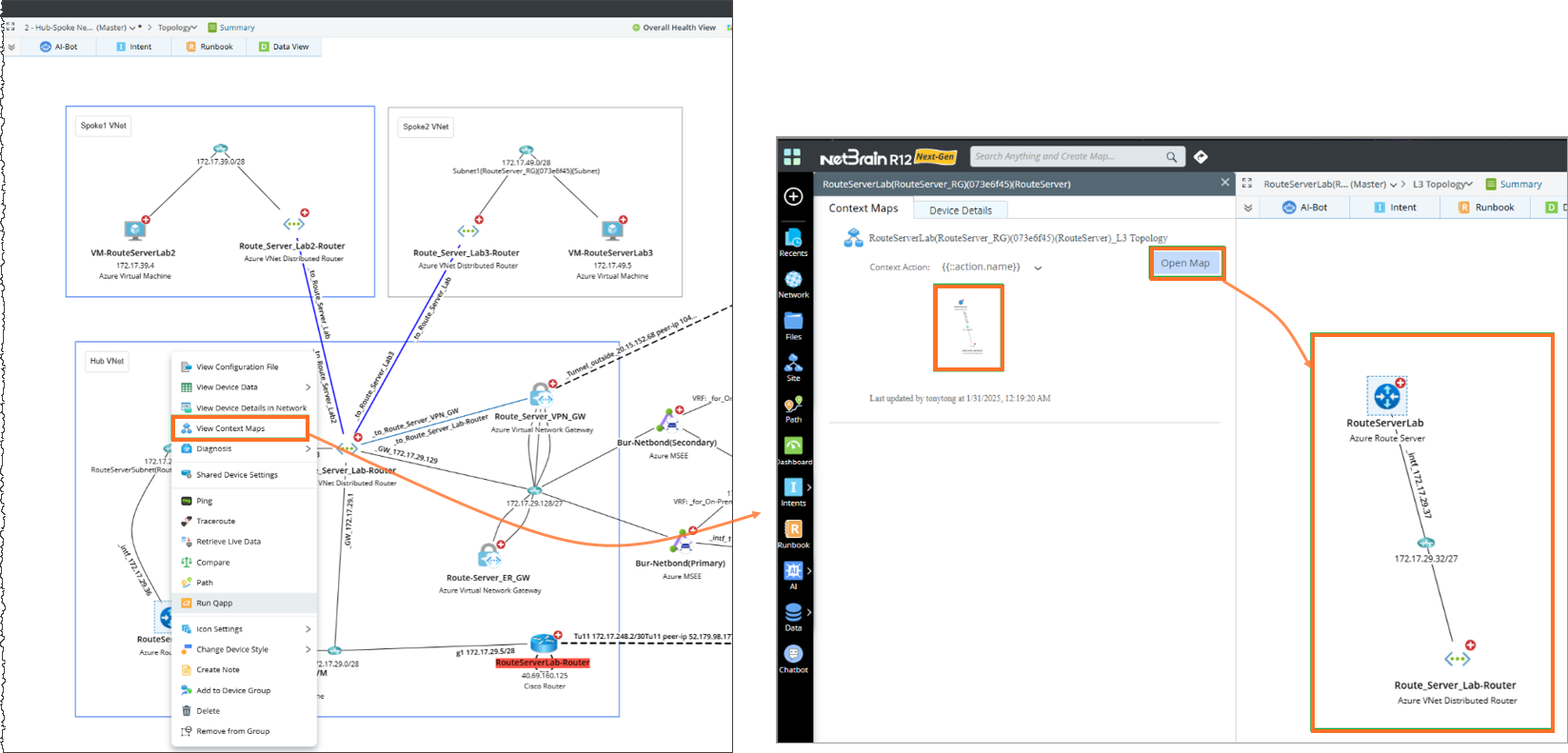
Device Details: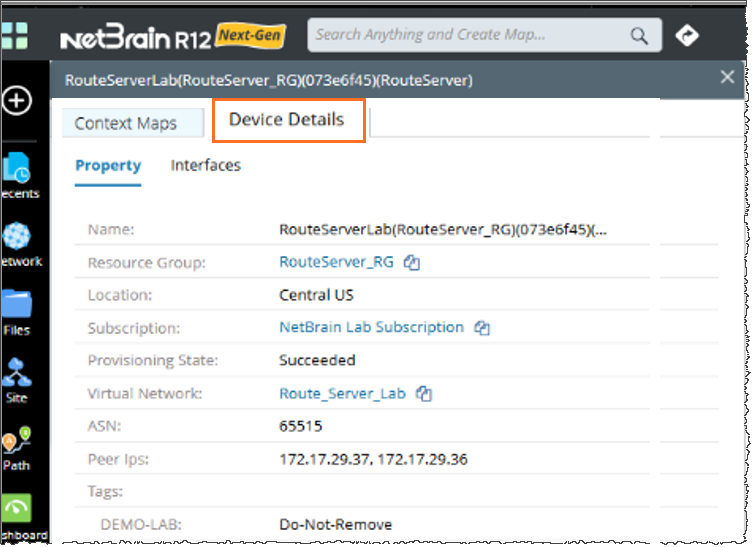
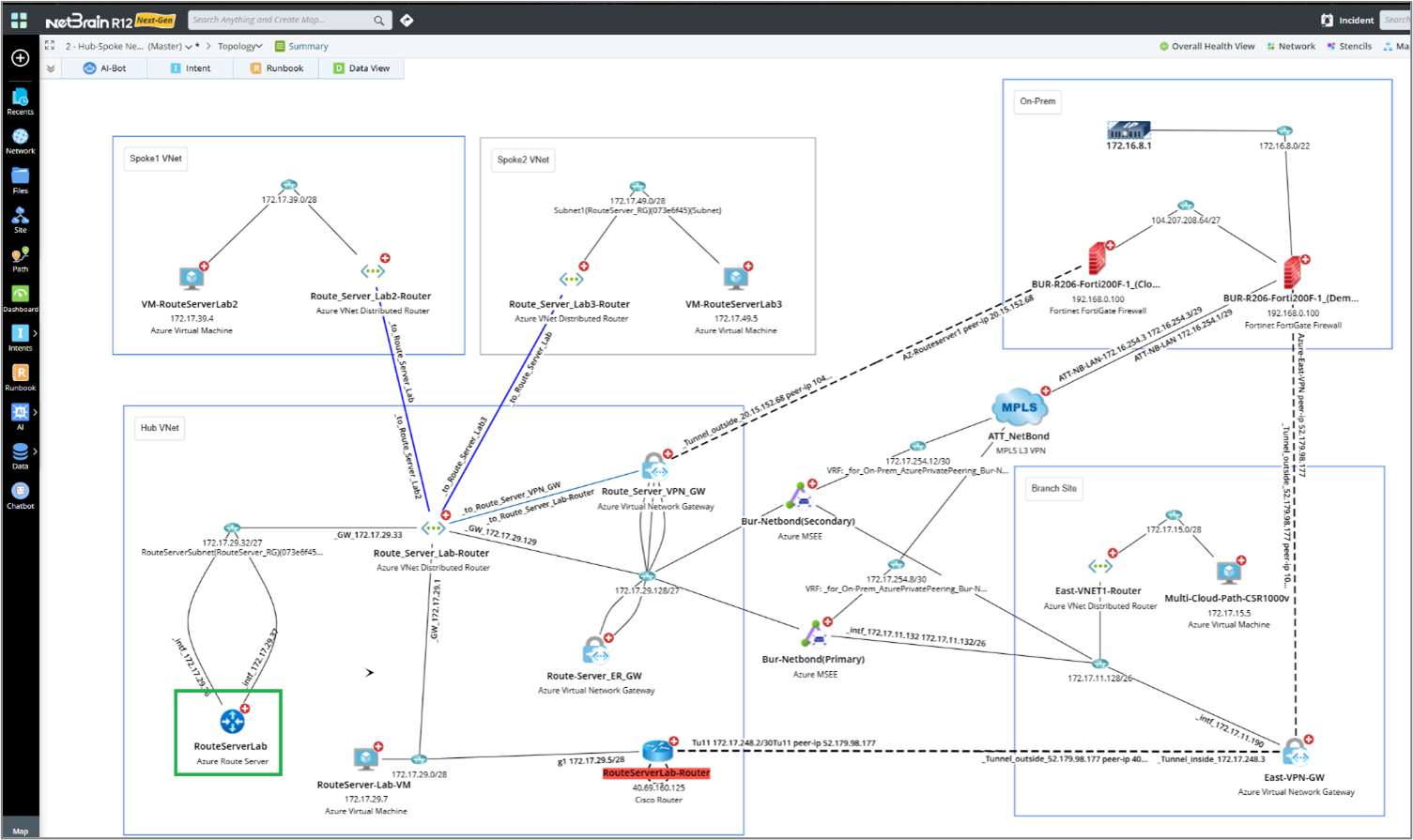
- Neighbor Topology: NetBrain provides visibility and insights into your cloud network, including Azure Route Server connectivity and topology.
The supported Azure Route Server connectivity options include:- Connection to a Virtual Network
- Connection to a BGP Peer (underlay)
- Connection within a Hub-Spoke network
- Connection within a Branch-to-Branch network
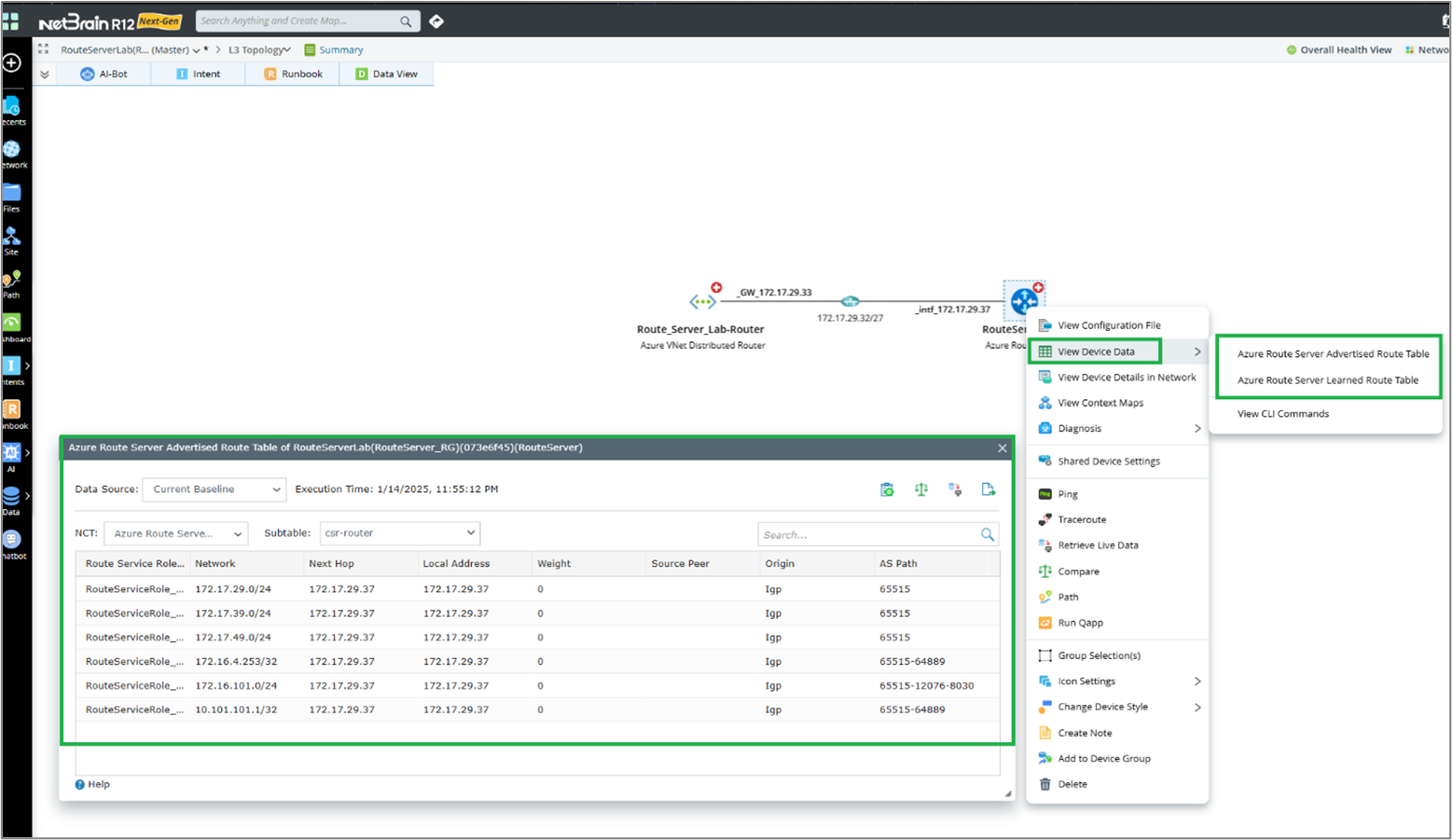
Data Table: NetBrain provides visibility into critical cloud network data through a dynamic map. Right-click the node on the map and select View Device Data to open the data table.
The data table displayed on the map includes the following:
- Azure Route Server BGP Advertised Route Table
- Azure Route Server BGP Learned Route Table
- Azure Route Server BGP Peers Table
- End-to-end Path
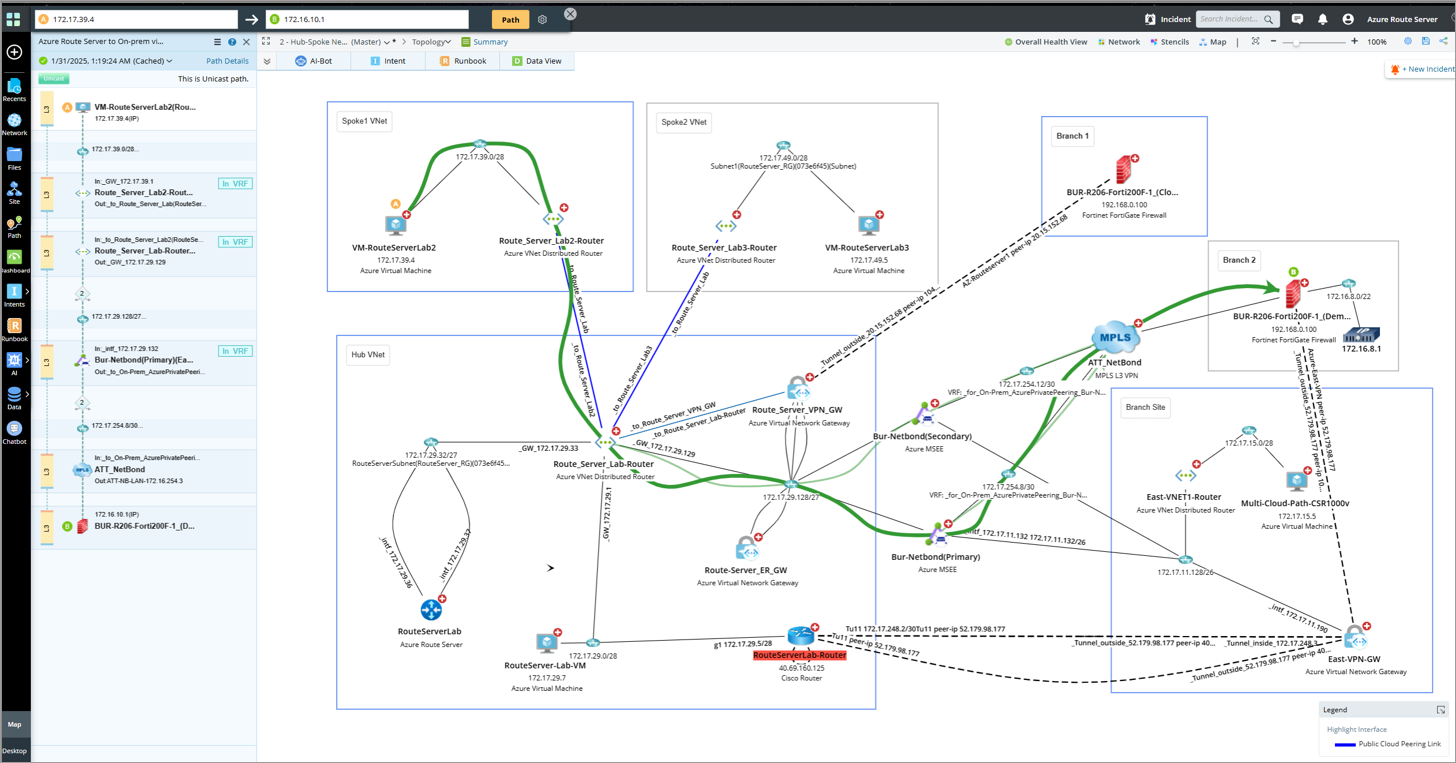
Enable branch-to-branch traffic path and configure route preferences to manage route learning and selection for the Azure Route Server.Branch-to-Branch Traffic Path:
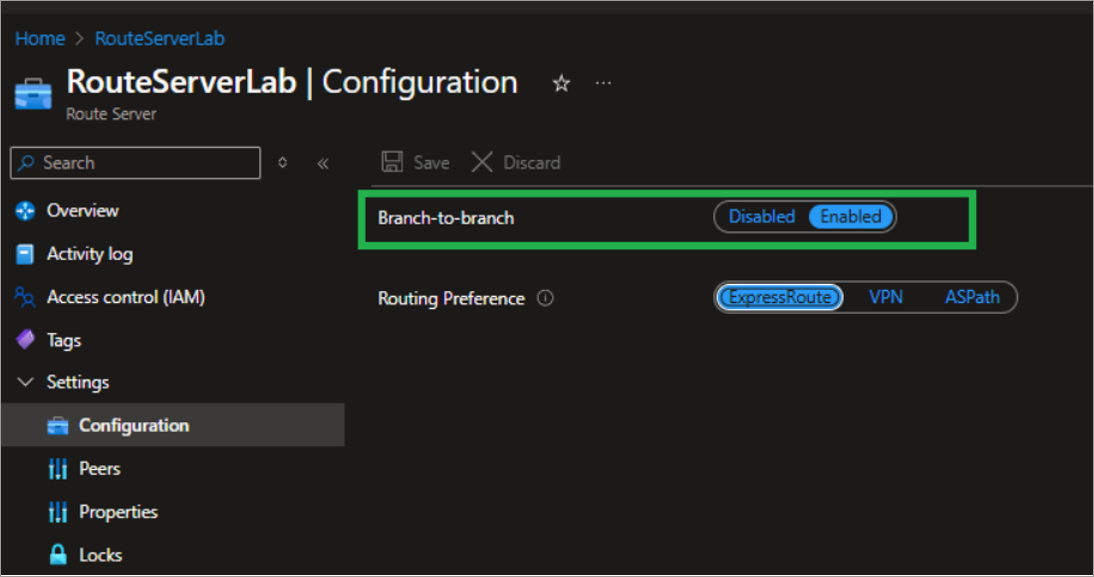
When branch-to-branch communication is enabled in the Route Server, the virtual network gateway and the Network Virtual Appliance (NVA) exchange their routes. NetBrain supports the corresponding branch-to-branch traffic path use cases, as shown below.
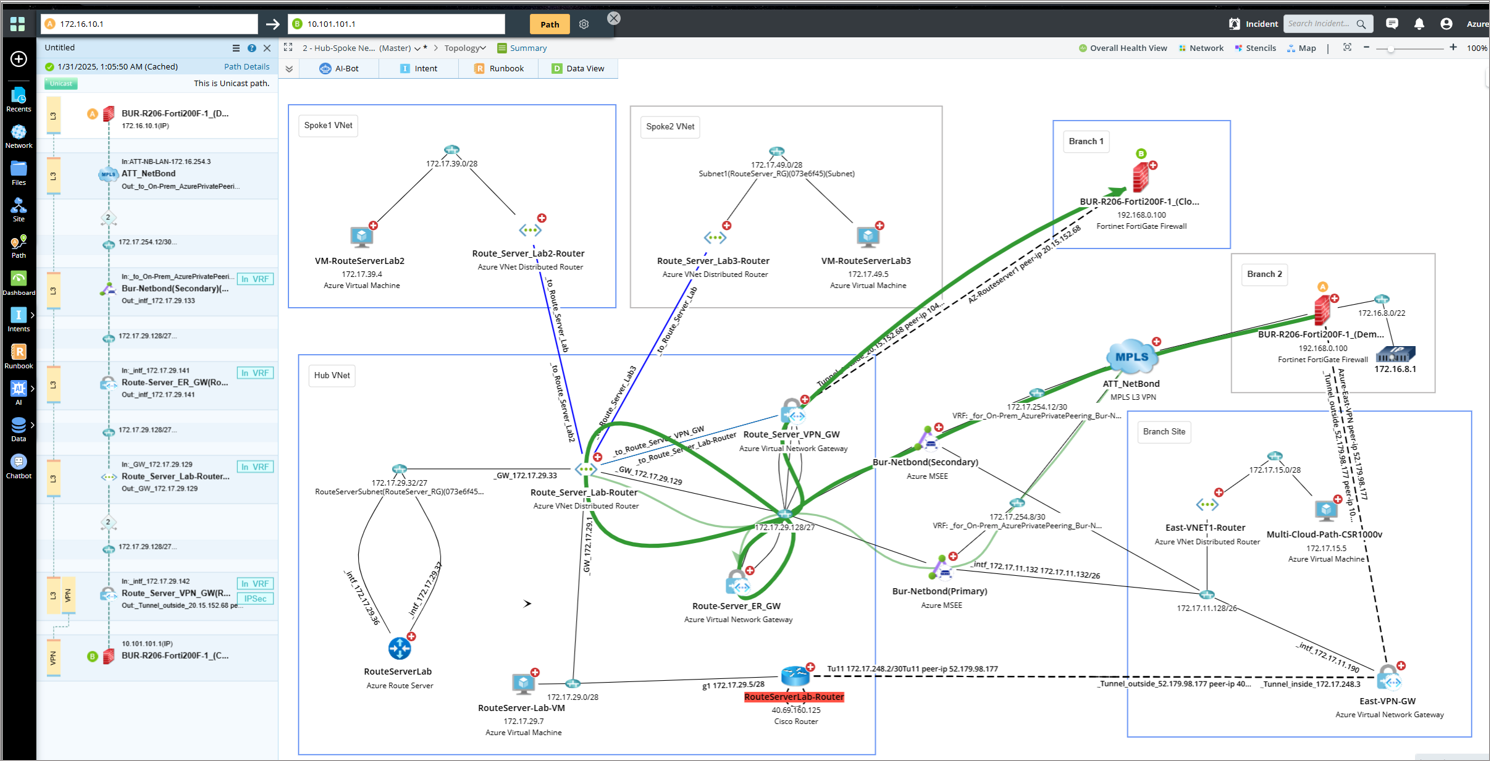
Routing Preference (ExpressRoute):
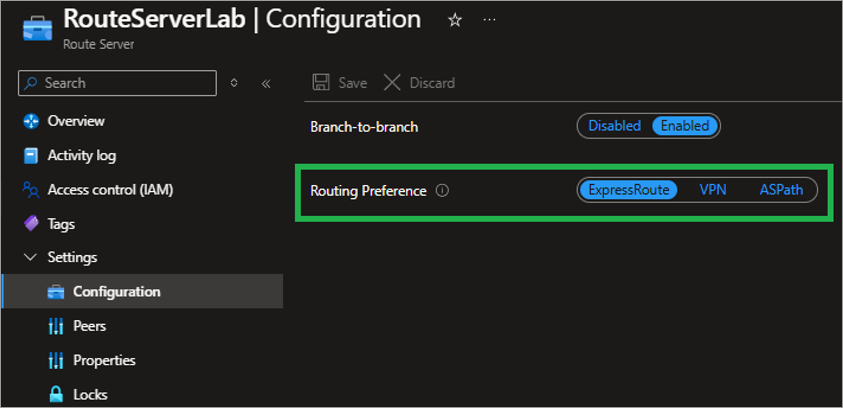
When Routing Preference over ExpressRoute is configured in the Route Server, it prioritizes learning routes from ExpressRoute connections. NetBrain supports the corresponding traffic path use cases, as shown below.
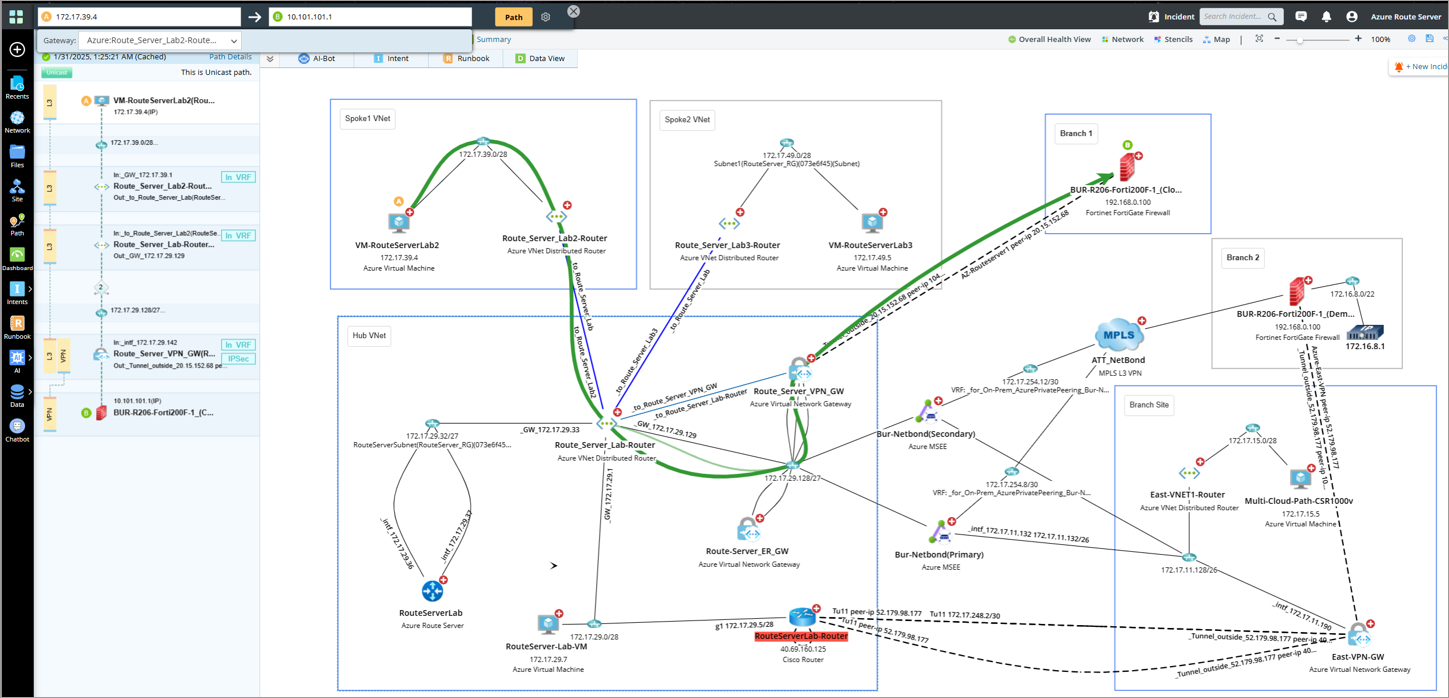
Routing Preference (VPN):

When Routing Preference over VPN is configured in the Route Server, it prioritizes learning routes from VPN connections. NetBrain supports the corresponding traffic path use cases, as shown below.
Routing Preference (AS Path):
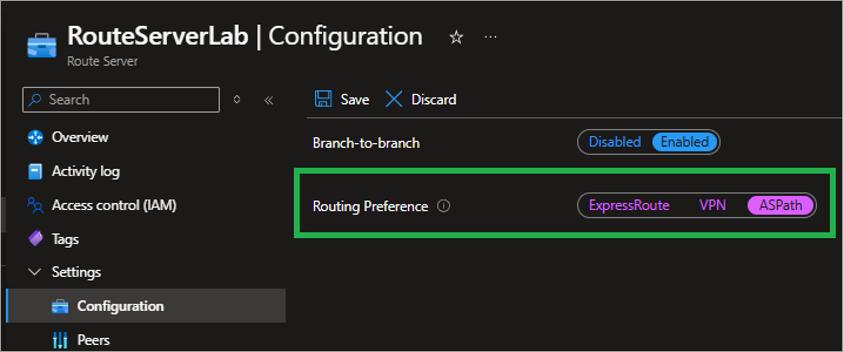
When Routing Preference over AS Path is configured in the Route Server, it prioritizes learning routes based on the Autonomous System (AS) Path. NetBrain supports the corresponding traffic path use cases, as shown below.
