Interactive Automation
Interactive Automation is when NetBrain intelligence records network engineers' diagnostic steps to create automation for their own use, enabling them to be more productive by getting data from multiple devices, looking for changes by executing a comparison automatically, and monitoring and getting alerts for threshold changes. It offers guardrails for any operator or engineer to make informed decisions based on network real-time status.
As networks get larger and more complex, automated documentation becomes more important, especially as networks incorporate technologies like SDN, SD-WAN, and public cloud. NetBrain not only provides end-to-end visibility across hybrid networks but also the ability to drill down into each segment and isolate network issues on a Dynamic Map that can be updated in real-time. This greatly accelerates problem identification and resolution. And when new devices are added or removed from the network, the documentation is quickly reflected in an updated network map which is exportable as diagrams to Microsoft Visio and Word.
With NetBrain, NetOps professionals leverage their own expertise to automatically record standardized procedures in a runbook as they detect, diagnose, and fix issues. The steps they use to diagnose issues, including the use of CLI commands on multiple devices, are automated in Runbooks.
Collaborative Automation
Collaborative Automation is where engineers and operators leverage the knowledge of peers with software that captures subject matter experts' knowledge to create executable automation units that others can then add to their own diagnoses. Expertise is available even when the expert is not. NetBrain helps when troubleshooting a problem, assessing the state of the network, or making sense of complex technology. It allows the NetOps staff to gather, analyze and visualize 1,000s of KPIs in seconds. It can be coupled with our collaboration capabilities to allow multiple ops teams (SecOps, DevOps, NetOps, ServerOps) to interactively resolve problems that span multiple technology domains without the need for time-consuming handoffs which result in delays. Everyone can get online at the same time and interact and make updates and remediations to the model through a shared analysis console

NetBrain captures and codifies the SME knowledge using Runbooks, Data Views, and Network Intents. Automatically capturing this information allows experienced engineers to codify and share their knowledge with junior staff, effectively shifting knowledge left, from experienced users to less experienced team members The next time the problem occurs, the runbook is executed by responders without in-depth knowledge or training. Even complicated network issues no longer need to be handled exclusively by experts. You are essentially using the knowledge of these highly skilled level-3 workers when they are otherwise unavailable (due to location or availability).
Incident Portal
NetBrain’s Incident Portal enables collaboration among multiple users working on the same troubleshooting task. An incident represents a ticket in NetBrain to track a network problem or a network change. End users can organize and share maps, devices, individual insights, and findings targeting a specific troubleshooting task and collaborate with more colleagues to resolve issues reducing MTTR. In addition, Incident Portal offers an independent portal page for each incident. External users without NetBrain Workstation seat licenses can access a portal to join the collaboration session by viewing maps and posting messages, etc.
The Function Portal feature enables network engineers to collaborate with their NetOps colleagues and with members of other operational teams who are not initially involved with a service ticket. This is one of the key approaches to achieving the goal of reducing service ticket overhead and improving team productivity and MTTR. With Function Portal, users from multiple teams (IT engineers, security engineers, etc.) work together to resolve complicated problems that would otherwise require hand-offs and wait for resources to become available.
Executable Runbook
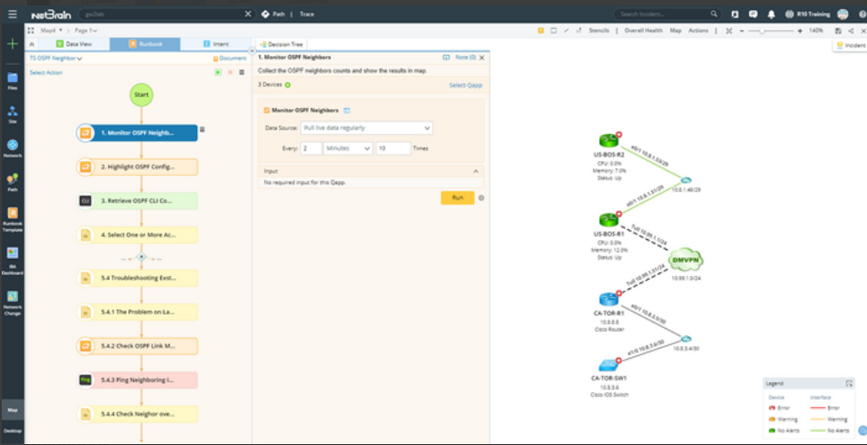
Executable Runbooks are a set of visual operational steps that engineers create by capturing their step-by-step workflows to allow the automation of future problem diagnosis, network data collection, and troubleshooting tasks. Runbooks provide a visual way to codify the network troubleshooting process into an executable, reusable, and documentable workflow, to elevate collaboration efficiency. Subject matter experts can digitize their knowledge into a runbook template to capture best practices and remediations that other operators can use. Once Runbooks are executed, the results can be shared with anyone in the organization, facilitating collaboration and enabling higher-level engineers to code their advanced knowledge into repeatable automation units.
Executable Runbooks At-A-Glance
▪Automate network operations on a large scale
▪Effortlessly collaborate with multiple engineers using the same Dynamic Map
▪Share and save network insights as to the groundwork for future troubleshooting
Guidebook
The manually defined Guidebook is a container that includes Data View Template, Runbook Template, and Network Intent to describe a troubleshooting process for a specific network issue. It can be dynamically qualified to match eligible devices. The guidebook is designed to replace users’ static troubleshooting playbook.
NetBrain also provides a low-code visual programming environment for users that are more comfortable or have previous experience with light programming approaches, writing scripts, and using other programming tools. Over time most users gravitate to NetBrain’s No-Code technology, but both types of automation can co-exist upon the same instance of NetBrain.

