Running a Network Intent at Backend Automatically
Like other automation objects such as Qapps, Network Intents can be scheduled to run at the backend automatically. More commonly, Network Intents are triggered to run by Flash Probe and 3rd-party system.
Triggered by Flash Probe
An NI can be installed as a triggered automation of a Flash Probe as part of Adaptive Monitoring Automation, a backend process to monitor the whole network's status periodically. When a flash alert occurs, the system will further execute NIs. You can view the triggered NI results with the flash probe via Decision Tree. For example, HRSP NI can be installed as a triggered automation of the HSRP state flash probe of the device BJ-L2-Core-A. When an alert occurs on the flash probe, you can trigger the NI to execute automatically.
Two ways to install an NI to a flash probe:
▪From Triggered Automation Management:

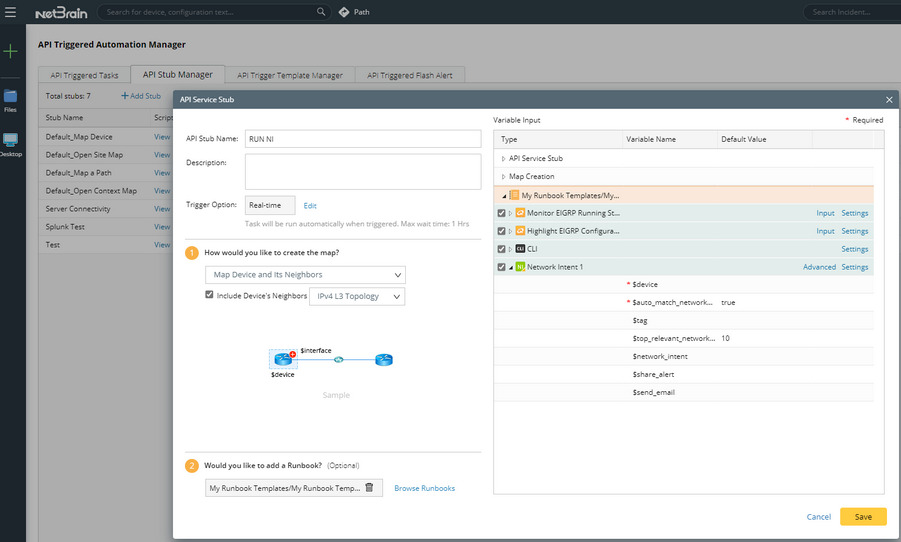
Triggered by 3rd-Party System
The typical use case is that the 3rd-party system will trigger NetBrain Runbook Template execution, including an NI node. For example, a ticket is created since a BGP neighbor of a core device is flapping, which triggers an API call to the NetBrain IE system, and the device name and BGP are sent to NetBrain as a keyword. A NetBrain Runbook can filter NIs related to this device and BGP and execute these NIs.
Two ways to define triggered NI by 3rd-party system:
▪Use Event Template to trigger NI: