Define Follow-up Triggered Diagnosis
Follow-up triggered diagnosis can be defined for each triggered diagnosis to run four types of intents (intent, intent template, intent cluster and ADT Intents). During follow-up triggered diagnosis, another intent is run at request when certain conditions are satisfied to complete a task.
In this chapter, the following example is described to illustrate how to define follow-up triggered diagnosis.
Example: Suppose the intent "Check Slow Application" is run several times and there is no alert, you can define follow-up triggered diagnosis to close ServiceNow ticket that triggered the automation. When there is alert generated, run the intent template "Auto Remediation" to remedy this issue.
Follow the steps below to define follow-up triggered diagnosis.
- In the Follow-up Triggered Diagnosis block, check the checkbox to enable this function. After this, the Follow-up Triggered Diagnosis block is no longer dimmed. You can start defining the follow-up triggered diagnosis.
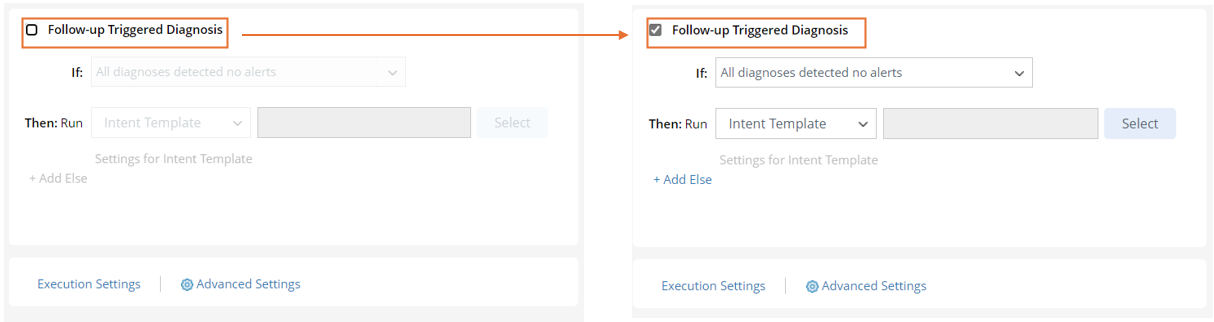
- Define the If condition: Click
 , then select one of the four options as the condition (in this example, the option "All diagnoses detected no alerts" is selected).
, then select one of the four options as the condition (in this example, the option "All diagnoses detected no alerts" is selected). 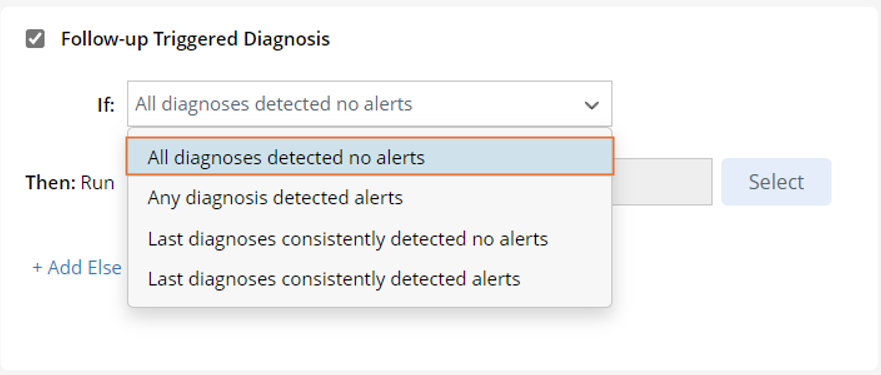
- All diagnoses detected no alert: The triggered diagnosis defined in the Triggered Diagnosis area generates no alert during the several rounds of execution.
- Any diagnosis detected alerts: Any round of executions of the triggered diagnosis defined in the "Triggered Diagnosis" block has generated alert, which indicates an issue.
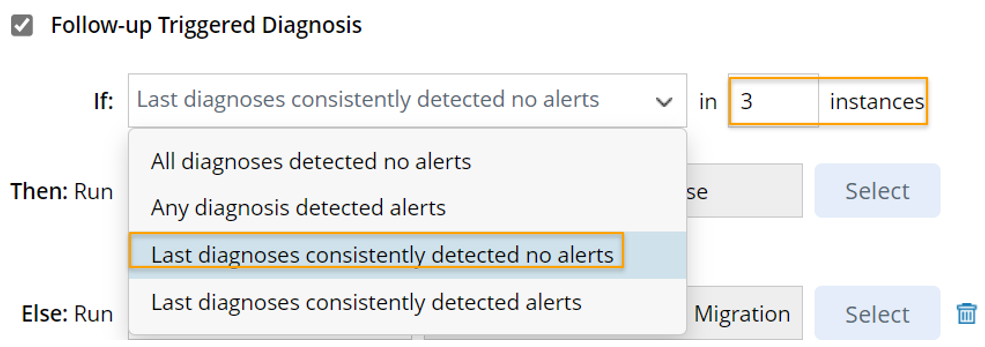
- Last diagnoses consistently detected no alerts: Trigger to run follow-up diagnosis if the last n main triggered diagnosis instances have no alerts. If Last diagnoses consistently detected no alerts is selected, you can set the number of instances of the diagnoses, and the range of this number is 1-9.
- Last diagnoses consistently detected alerts: Trigger to run follow-up diagnosis if the last n main triggered diagnosis instances have alerts. If Last diagnoses consistently detected alerts is selected, you can set the number of instances of the diagnoses, and the range of this number is 1-9.
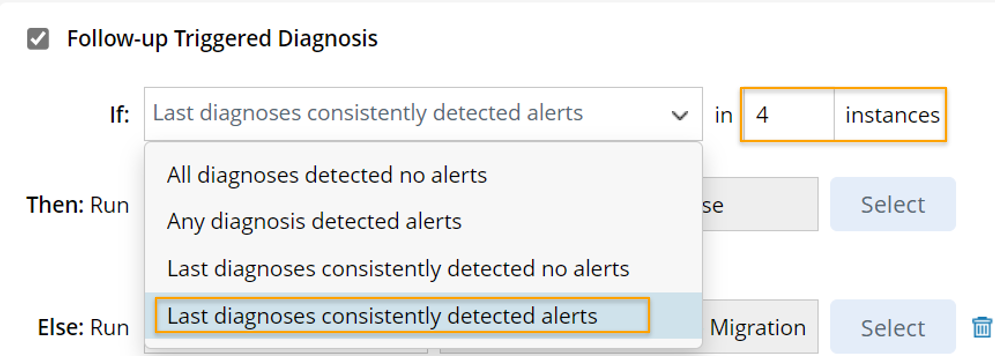

Note: With the Last diagnoses consistently detected no alerts and Last diagnoses consistently detected alerts options, the system can decide whether to run follow-up triggered diagnosis in TAF after running the main triggered diagnoses several times to check whether it has alerts or not.
- Define the Then logic: In the Then block, click
 to select one type of intent, then click Select to select the intent to run when the If condition is satisfied. For example, you can select to run the intent snow_webhook_auto_close to close the Ticket.
to select one type of intent, then click Select to select the intent to run when the If condition is satisfied. For example, you can select to run the intent snow_webhook_auto_close to close the Ticket. 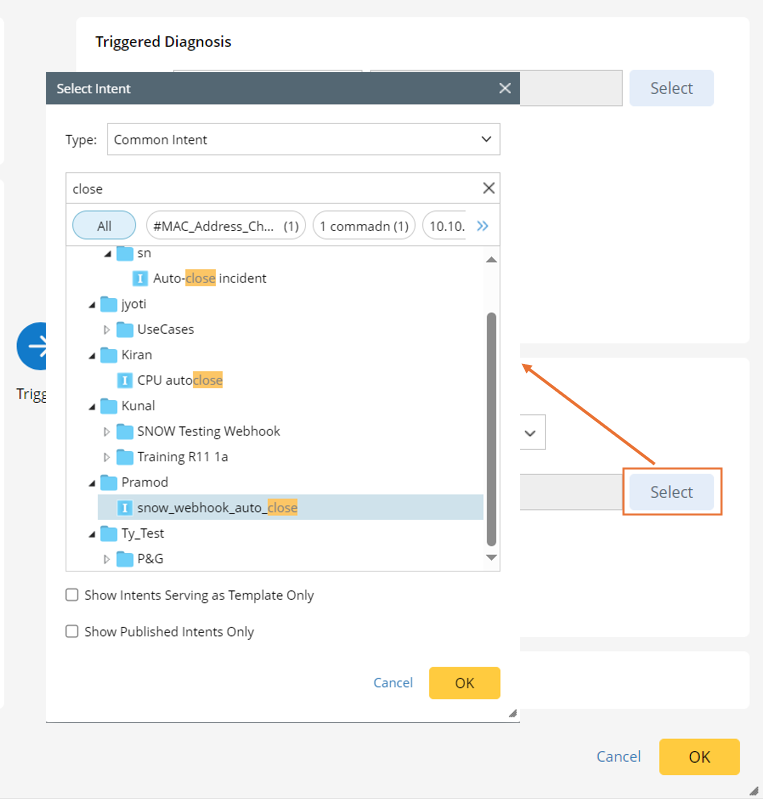
After selecting the intent snow_webhook_auto_close, you will be directed to the Settings for Intent-based Triggered Diagnosis dialog to further define the conditions for executing the selected intent (for detailed steps, see Intent-based Triggered Automation). Or you can click Settings for Intent to open this dialog.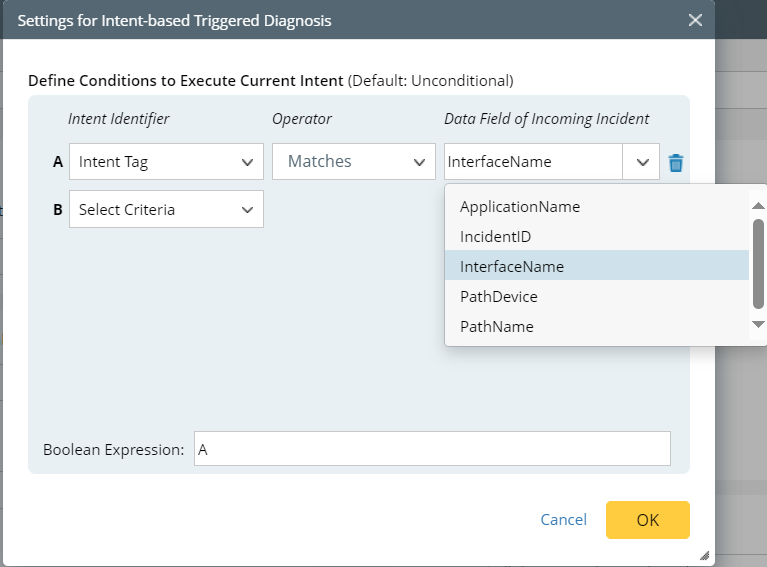
- Add the Else logic: Click the + Add Else link to add Else logic.

- Click
 to select an intent/intent template/intent cluster/ADT intents to run when the If condition is not satisfied. Then click Select to select the intent. In this example, intent template #08-004-1_Remediation - Migration - EBS Volume Type to GP3 is selected.
to select an intent/intent template/intent cluster/ADT intents to run when the If condition is not satisfied. Then click Select to select the intent. In this example, intent template #08-004-1_Remediation - Migration - EBS Volume Type to GP3 is selected. 
- Click the Settings for Intent Template link to configure the intent. In this example, you will define the settings for the triggered diagnosis of the intent template #08-004-1_Remediation - Migration - EBS Volume Type to GP3 (For detailed steps, see Intent Template-based Triggered Diagnosis).
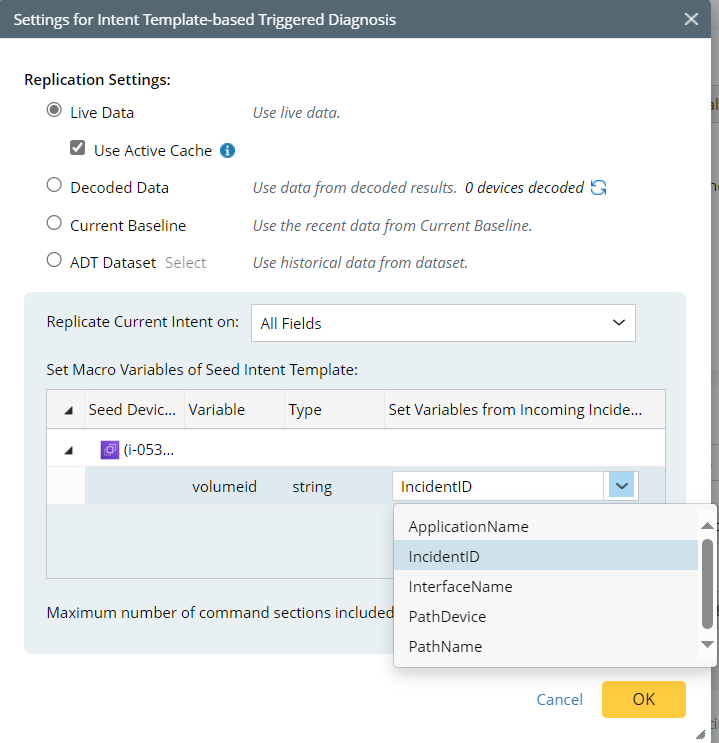
- Click OK.
- Click