Neighbor Pair Replication Settings
Complete the following steps to define the neighbor pair replication logic.
- Select the Enable Neighbor Pair Replication checkbox to enable it and click Settings to open.
-
Manually assign the hub and spoke roles to the seed devices, specifying their dependency relationship.

Note: The system can distinguish the hub devices and the spoke devices based on the logic defined in them. Therefore, if you assign the device roles incorrectly, you will be reminded. -
Define an alias for each seed device to display under the Replication Settings section inside the intent, making it convenient for you to view.

Note: Alias definition is optional, and the alias does not need to be unique. - For each hub device, you can select tables from the following three sources to build the table for neighbors, which determines how the corresponding neighbors are discovered.
- Device Table: The neighbors are discovered from a table parsed from the command results of hub devices (parsed table) and etc.
- Automation Data Table: Select the columns with Hub device and Neighbor device information in the ADT to build the neighbor table.
- Topology Table: Select one of the topology types to build the neighbor table.
-
Device Table
When you select a table from the Device Table, all the tables in the hub devices will be listed in the Neighbor column for you to select, such as the parsed table, built-in table, merged table, and all other compound tables. The macro variable is supported in the command of the neighbor table, which will be explained in detail in Define Macro Variables for Hub and Spoke Devices.
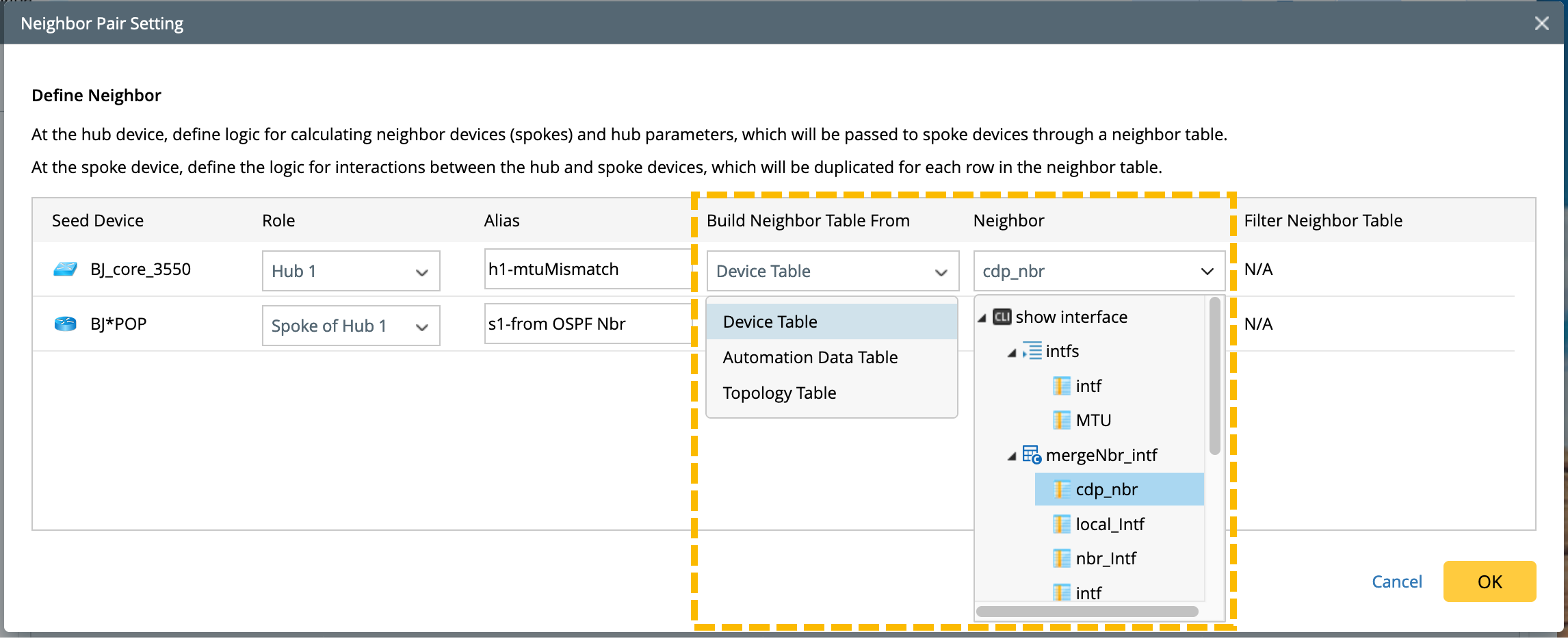
Neighbor Discovery Logic: If the IP addresses are selected as the neighbor column, the system will directly use these IP addresses as the hostname to discover the neighbor devices. When no devices are discovered, then use them as an IP to check whether there is an IP address match.
-
Automation Data Table: When selecting ADT as the data source of the neighbor table, you need to:
- Specify the table column used to find neighbors. The columns containing device information in the ADT will be listed for you to select as the Neighbor column.
- Specify the device key column in the selected ADT to find the corresponding hub device. That is, you can select the columns in the same ADT as the Hub Device Key Column to clarify the relationship between the current device (hub device) and its neighbors.
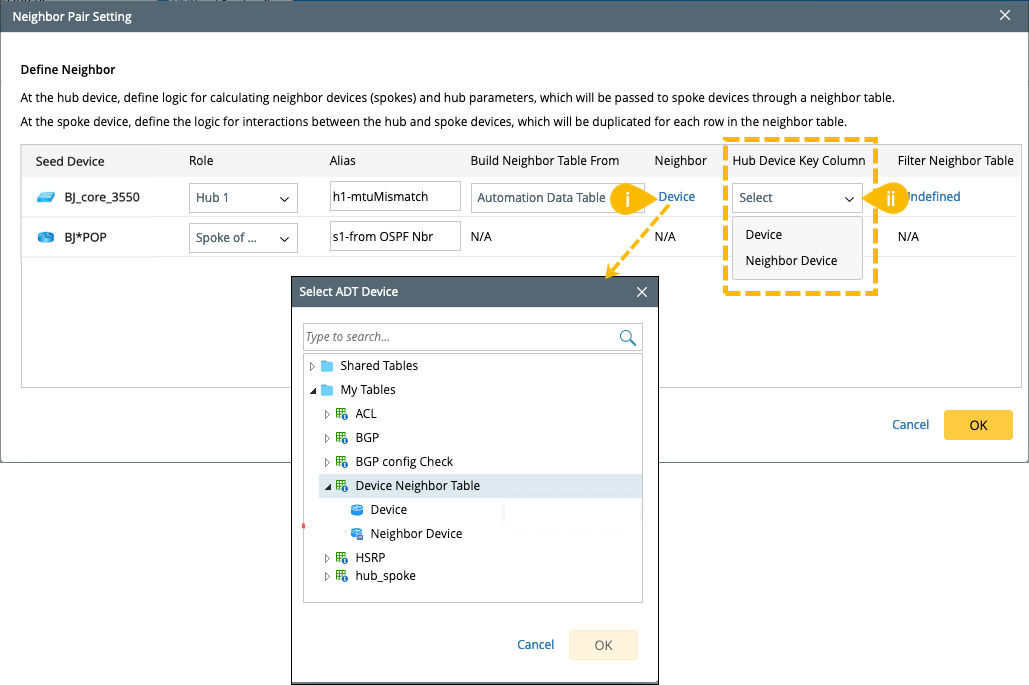
Neighbor Discovery Logic: Use the incoming devices to match the hub device through the device key, and then find the neighbor devices based on the relationship to the hub device in the ADT. If there are multiple devices contained in the device column in the ADT, and more than one hub device is matched, then all the discovered neighbor devices of the matching hub devices are available.
-
Topology Table: You can also select a topology table to build the neighbor table. Three topology types are supported: IPv4 L3 topology, IPv6 L3 topology, and L2 neighbor.
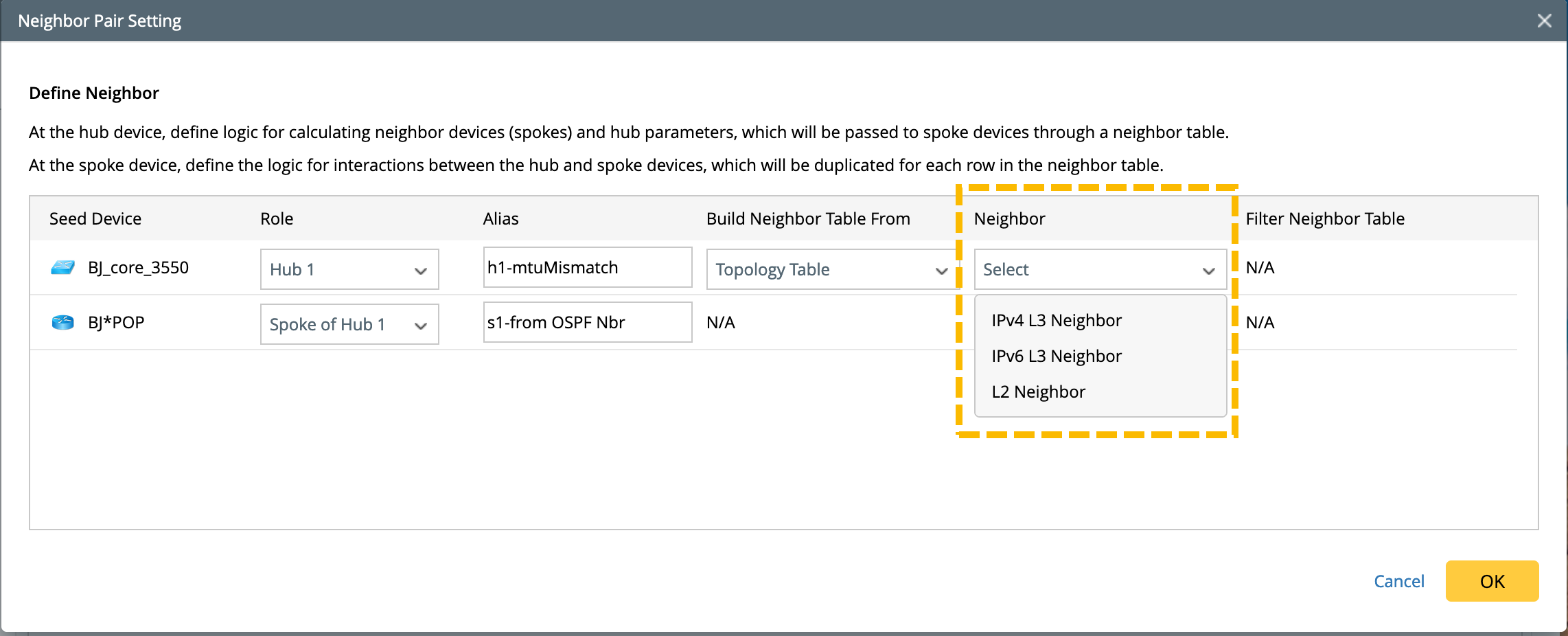
Neighbor Discovery Logic: Once you select a topology type, the topology table implies the relationship between a device (hub device) and its neighbors. The neighbor devices correspond to the devices in the Neighbor column in the topology table.

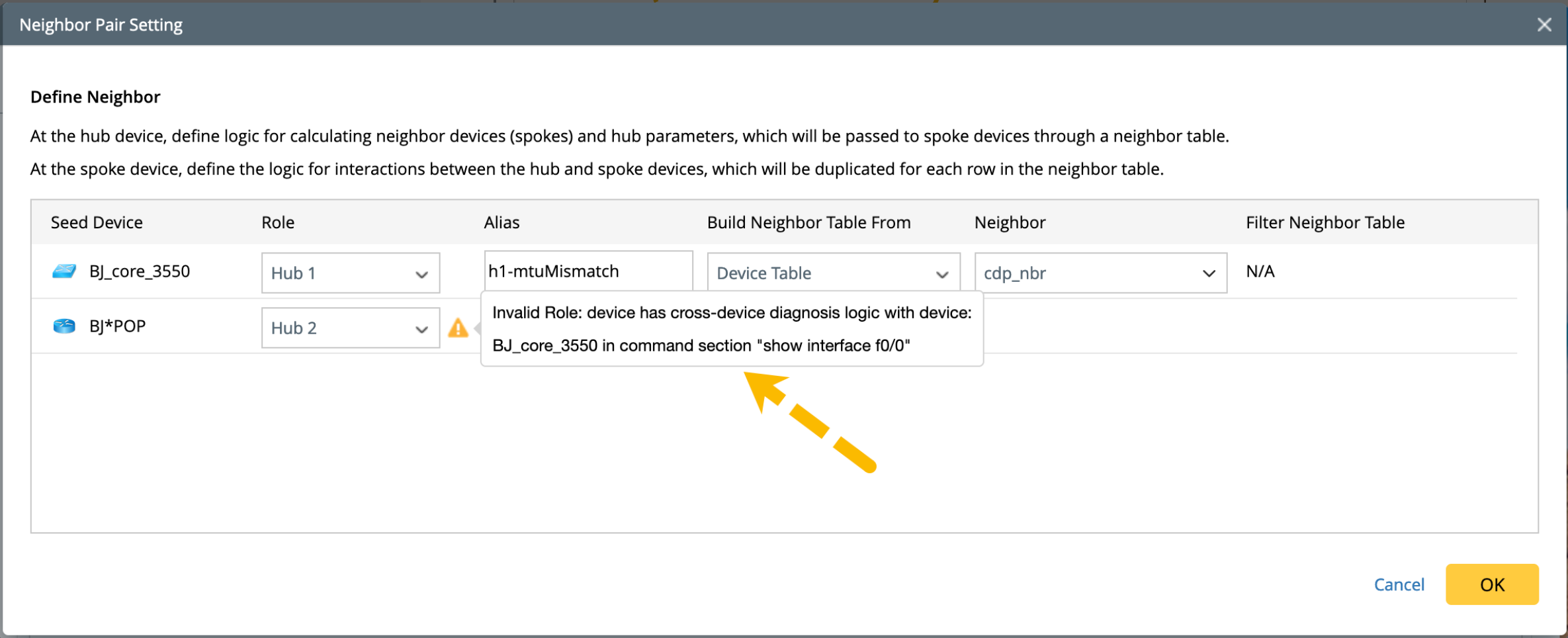
After the above definition, you may need to define the macro variables for hub and spoke devices separately as required. There are two main use cases depending on whether the command in each hub device has a macro variable.
- Use Case 1: The spoke device has a macro variable defined, but the hub device does not.
- Use Case 2: Both the hub device and spoke device have macro variables defined.