Intent-Based Continuous Network Assessment and Collaborative Troubleshooting
Network Intent (NI) is an automation construct that allows users to define expected design and operational state. It establishes a baseline configuration and operational state to validate the network design. There are two main intent-based automation workflows: Continuous Assessment Workflow and Collaborative Troubleshooting Workflow.
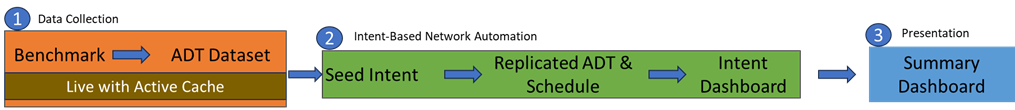
In the continuous assessment workflow, the data is collected through the benchmark and saved in the ADT dataset. The Automation Data Table (ADT) is a global data table to store the network-wide assets, associated intents, intent dataset and results. The ADT dataset is used to decode, replicate and run intents. The results are presented in the Summary Dashboard.
The collaborative troubleshooting workflow starts with mapping the problem area, similar to map-based interactive automation. Different levels of users can create intents via the Quick Intent tab within the map and run intents to troubleshoot the same problem. The active diagnosis results and the relevant triggered event results can be shared in a Summary Dashboard.

From the end user's perspective, the output of intent-based automation is the sharable Summary Dashboard, in which users have a high-level view of network assessments or a network problem and can dive into the diagnosis detail. The underlying systems to support intent-based automation have four essential subsystems:

- Intent Creation: where diagnosis know-how is turned into automation assets across the entire network in the form of Network Intent (NI). Intent can be created via Quick Intent within a map whenever users need it or from a full-scale Intent Manager proactively.
- Intent Replication: where the seed intents are replicated through the whole network. The majority of the intents can be replicated with a simple template (NIT) by the Intent Replication Wizard.
- Intent Installation: where various automation assets are connected to the problem diagnosis through Triggers from the ticket system, human interaction, or Intent Timer.
- Intent Execution: where automation is executed in response to an external symptom in three successive methods, namely triggered, interactive, and preventive. All execution output can be viewed by Intent Dashboards, and a Summary Dashboard can be created for a set of Intent Dashboards.