Create an API Parser
This section introduces API parser, which is for retrieving and parsing data from a third-party system via API.
The following example shows how to create an API Parser to extract key metrics from a Cisco ACI network. And the functions and logics used will be explained as you walk through this example.
- Go to Parser Library, then click New Advanced Parser from the drop-down menu of a folder. The parser editor will open.
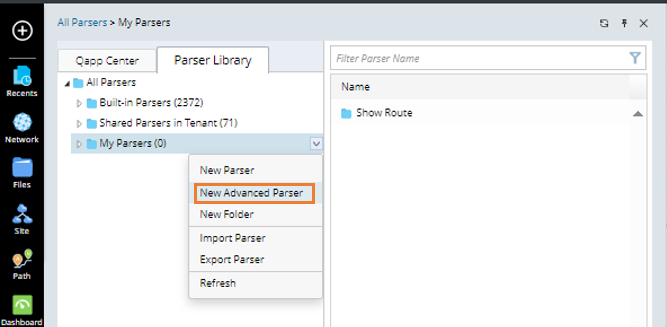
- Keep the default Traditional Devices option from the Qualified Device list, select Cisco ACI APIC from the second list.
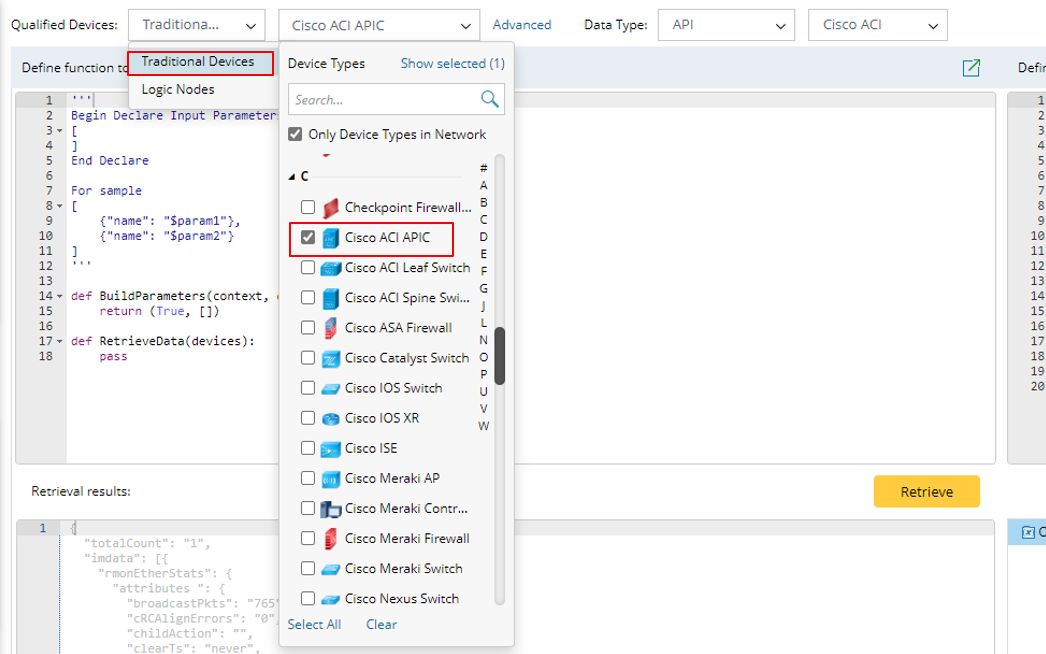
- (Optional): Click Advanced to configure the settings for filtering applicable devices as qualified device. For more information, see Qualified Device Filter in Advanced Parser.
- Select a specific data type. In the Data Type field, select API from the first pull-down list and Cisco ACI from the second pull-down list.

- Define the retrieve script which is for obtaining parser sample. the retrieve script consists of three major parts:
- Retrieve parameters: Manually input parameters required for data retrieval. The parameter values will be converted to parameters for the Build Parameters Function.
- Build Parameters function: Build the parameter objects used by the Retrieve Function. The values of the Build Parameters Function are device objects.
- Retrieve function: This function primarily serves for defining the scripts for retrieving sample data. The scripts will be submitted to the API server to be run.
| No. | Function Name | Explanation | ||
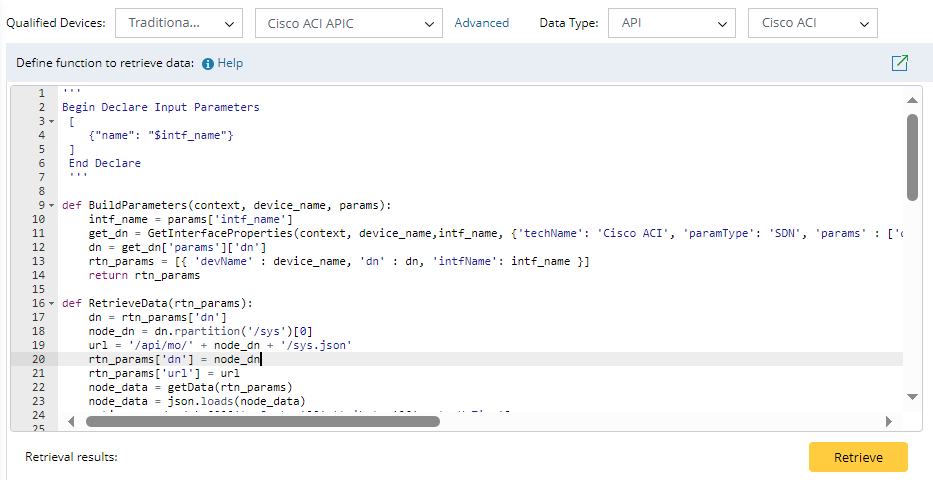
| 1 | Declare Parameters | This function is to declare the parameters from user inputs at runtime. This function is in the JSON format, and a sample code is as follows: ''' The item name defined in this function refers to the name of the parameters (variables) that receives values from user input. | ||
| 2 | def BuildParameters (context, device_name, params) | This function declares the parameters from GDR, DeviceSetting, and SDN. It contains three fixed parameters:
This function also supports calling built-in APIs to get device or interface parameters:
The type of returned values by this function is tuple (bool, list).
| ||
| 3 | def RetrieveData(devices) | This function is used to retrieve the data of devices based on the parameters declared in the Declare Parameters and BuildParameters functions. This function contains one parameter. The following is a sample code of this function:
|
- Click Retrieve and select a device to retrieve data on this device. The system will firstly retrieve parameters, and a window will pop up for selecting devices. In the retrieving process, the system will verify the following:
- The retrieved text is in complete and standard format (for example, standard Json format).
- The "name" parameter exists.
- Each parameter has its unique name. There is no parameter name duplication.
- Define the parser scripts to parse key metrics from the retrieved data. The parser scripts contain two parts: variable tree and parser function. Define these functions step by step:

|
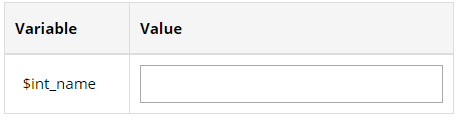
Note: After selecting device, a window for defining parameter will display for selecting/inputting parameter value. For $intf_name, you can select the parameter value. |
| No. | Function Name | Explanation | ||
| 1 | Declare variable tree | This function declares the metrics (variables) and the types you want to parse from the retrieved device data and generates a variable tree. The following parameters of a variable are defined:
This function is in the JSON format, and a sample code is as follows: ''' | ||
| 2 | def ParseText (original_result) | This function returns the specific metric values and assigns the values to corresponding variables in the variable tree. The following is a sample code of this function:
|
- Click Parse Results, then the parsed results will be added to the pane below:
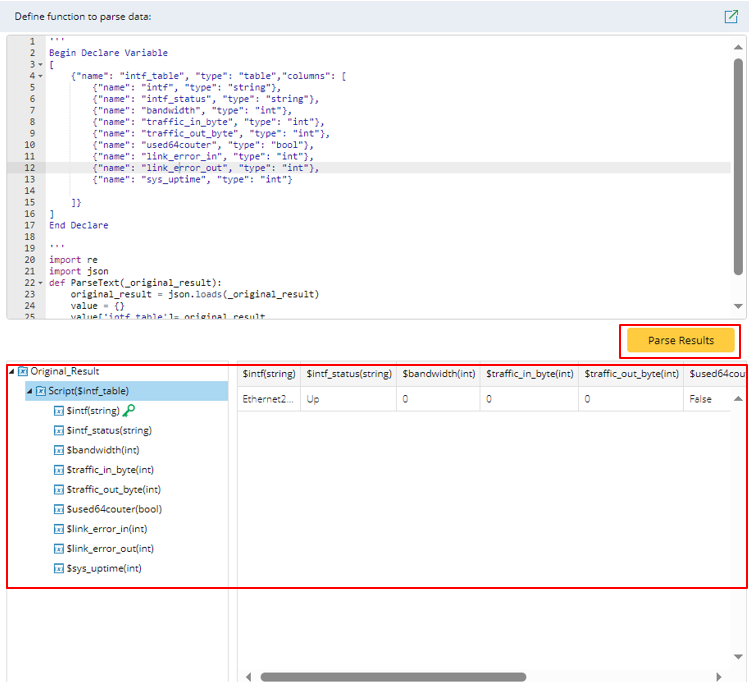

Note: In the parsing process, the variable tree will be verified in the following aspects:1) The variable tree is in complete and standard Json format. 2) The variable tree contains name, type parameter. When it is table type, it contains column parameter. 3) Each of the variables at the same level have unique name. There is no variable name duplication for variables at the same level. 4) The variables are in the range of values for its type.
- Click
 at the upper right corner of the page. The Parser will be saved in the Parser Library.
at the upper right corner of the page. The Parser will be saved in the Parser Library.
See also: